Brazed Cold Plate
Brazing is a method of connecting the welds by using a metal brazing filler metal with a lower melting point than the weld metal, heating the weldment and the brazing filler metal to a temperature higher than the brazing filler metal and lower than the melting temperature of the weldment, and using the liquid brazing filler metal to wet the weldment metal, fill the joint gap, and diffuse with the parent metal.
Brazed Cold Plate
Process introduction:
Two metal plates with internal channels (heat dissipation fins can be added inside) are processed, and solder is filled and laid between the two metal plates. The filling solder with a lower melting point is melted to the welding surface through capillary action at high temperature by brazing process, and the two metal plates with internal channels and fin structures are connected to form a whole with an internal flow channel, which is processed into a liquid cooling plate after mechanical processing and surface treatment.

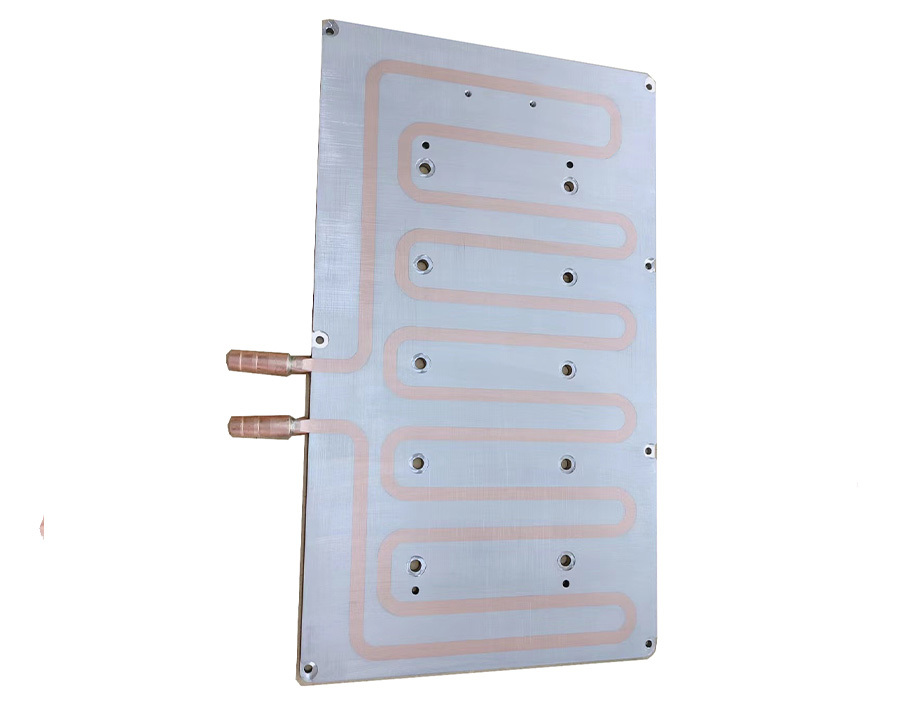
Brazed liquid cooling plate structure

Brazed liquid cold plate cross section
Design Parameters
Common materials for brazed liquid cooling plates: Al1100, Al3003, Al6061, Al6063, Cu1100, Cu1020.
Internal fin structure: machined fins, folded fins, stamped fins, extruded fins, Skived fins

Vansim provides more reference suggestions for your brazing cold plate design.
Contact Us >>Application status:
The brazed liquid cold plate has high welding reliability, the internal flow channel size and path can be freely designed, the heat exchange efficiency is high, and heat sources can be arranged on both sides of the cold plate. It is very suitable for thermal management products with high power density, irregular heat source layout, and limited space; the one-piece aluminum structure can be applied to a variety of surface treatment methods. Brazed liquid cold plates require special welding fixtures, and the process threshold is relatively high.

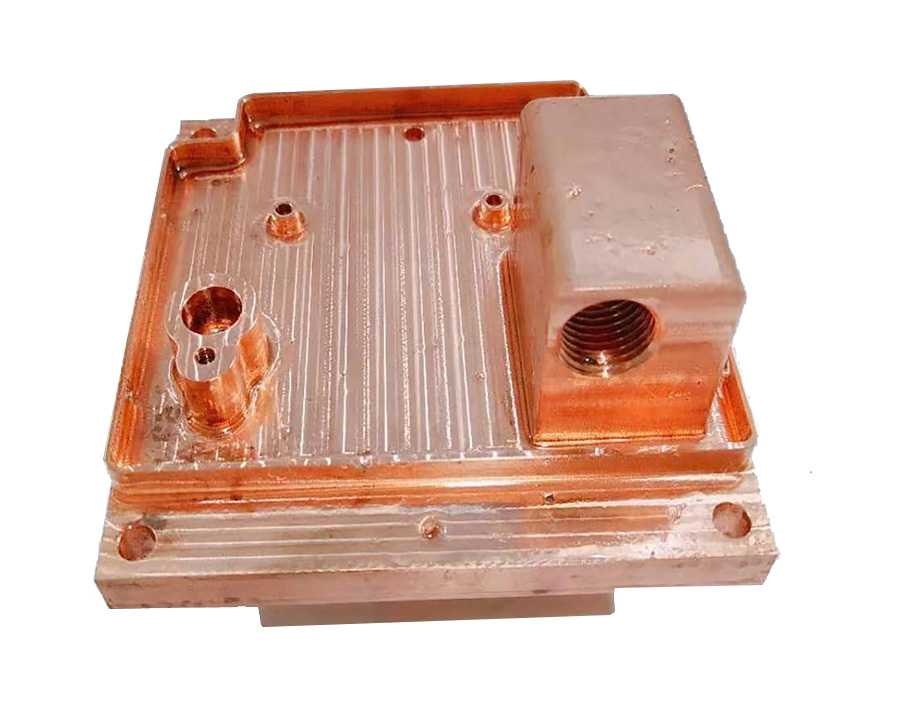
Brazing water block for Data Center cooling system
Tunnel furnace welding process: The weldment enters the furnace from the feeding section, passes through the preheating zone, heating zone and cooling zone, and finally reaches the discharging section to complete the welding.
It can be protected by gas filling or vacuum, and used in tunnel furnace for continuous mass production. It is suitable for mass production of CPU water cooling heads. It is small in size, easy to operate, and has high stability.
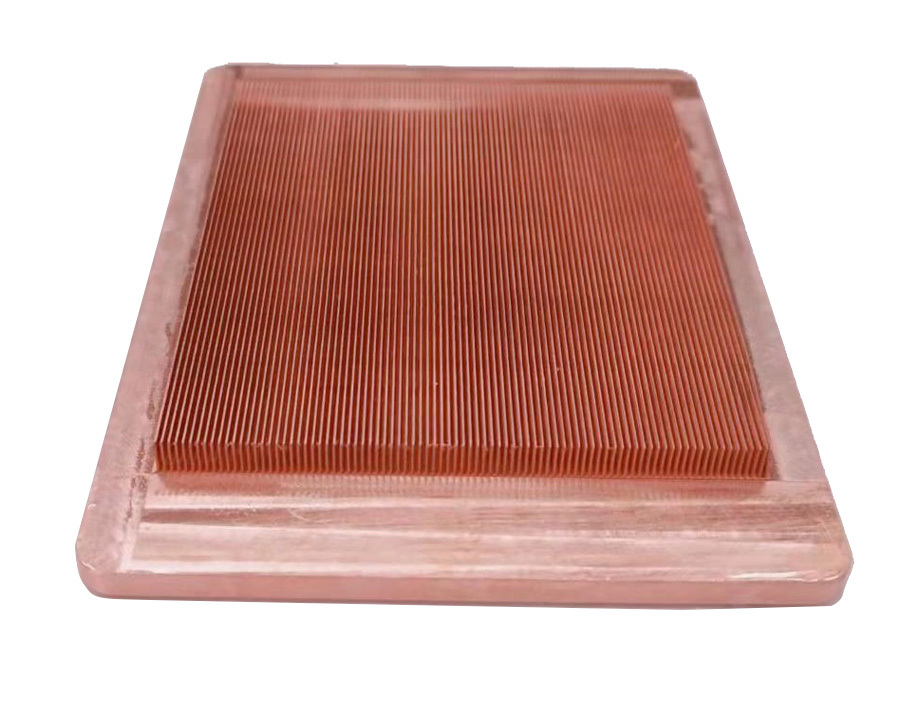
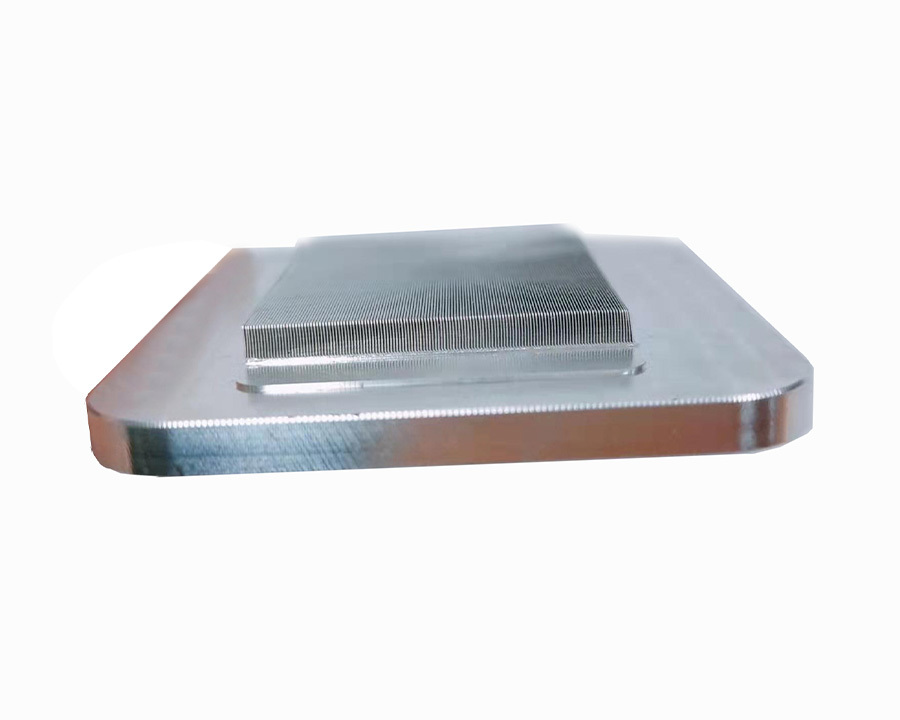
Micro-channel copper skived fin heatsink + copper base
After brazed process
To be a water block or after CNC machining to complete final process



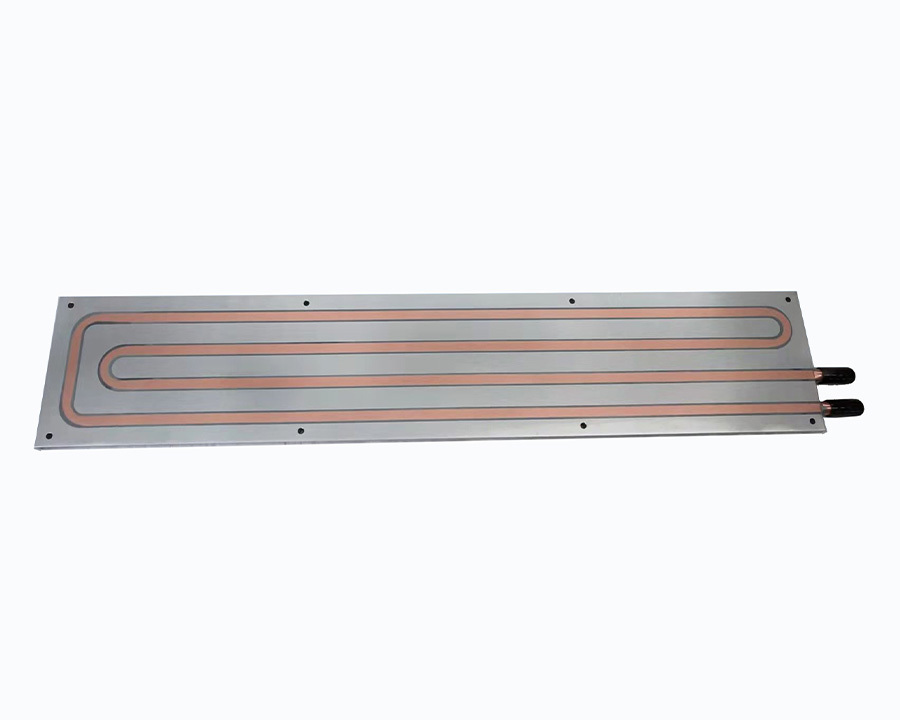
Brazing liquid cooling plate used for new energy battery cooling system
The battery cooling system consists of several important components, including batteries, battery coolers and water-cooled plates. There are two main types of brazed water-cooled structures: water-cooled plate structures and direct-cooled plate structures. They are usually brazed from two upper and lower O-state aluminum sheets. This design allows the antifreeze to flow through the stamping flow channel structure, thereby continuously cooling the battery.
In the selection of water-cooled plate materials, material strength and product corrosion resistance are the main considerations. By combining high-strength composite materials with water-cooled plate structures, the effect of thinning and reducing costs can be achieved. The development of composite materials and the requirements for lightness and thinness have limited the conditions of other welding methods to a certain extent, so brazing is currently the most commonly used welding method.

CNC machined plate or stamping plate + flat plate

After brazed process

To be a battery cooling plate

Other process thermal products reference :