Laser Cooling
The cooling method of the laser usually depends on its power, application requirements and working environment. Vansim provides you with heat sink and water cooling plate manufacturing for different process types of air cooling and liquid cooling solutions.
Which parts of the laser cooling system need to be cooled?
Usually, the laser cooling system needs to cool the following parts,
These components will generate a lot of heat during the operation of the laser. If the heat is not dissipated in time, it may cause the laser performance to deteriorate or even be damaged.

1. Laser pump source
The laser pump is the energy source of the laser. Its working principle is to input energy into the laser tube so that the laser generates laser. Therefore, in the laser cooling system, the laser pump needs to be cooled to ensure that it can continue to work.
2. Laser tube
The laser tube is one of the most important parts in the laser and is also the part that is most susceptible to heat. Therefore, in the laser cooling system, the laser tube needs to be cooled specifically to ensure that its temperature is not too high.
3. Laser lens
The laser lens is an important part of the laser optical path and is also one of the parts that are most susceptible to heat. Therefore, in the laser cooling system, the laser lens needs to be cooled to ensure that its temperature is not too high.
4. Laser optical components and electronic components
There are many electronic components in the laser, such as power supply, controller, etc. These components also need to be cooled to ensure that they can work properly.
Heat dissipation structure and technology Semiconductor laser:
Usually a welding layer is used to connect the chip and the heat sink together, and high thermal conductivity materials such as gold-tin solder are used to improve the heat conduction efficiency. Fiber laser: The pump source and optical components on the optical module are installed on an aluminum alloy base, and the cooling water flows through the holes on the base to directly cool the base. Through the use of these heat dissipation structures and methods, the temperature of the laser during operation can be effectively reduced, ensuring the stable operation of the laser and extending its service life.
How to choose the cooling method for the laser?
The cooling method for the laser needs to consider the laser power, operating time, ambient temperature and application requirements. Some high-power or long-running lasers usually require a more powerful cooling system to ensure the stability and life of the equipment.
What can Vansim do for your laser cooling system?
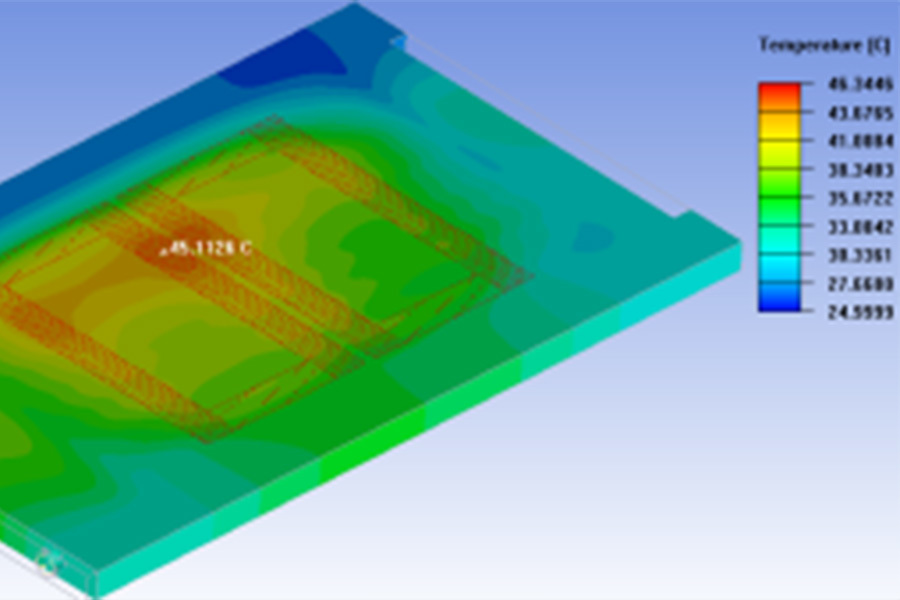
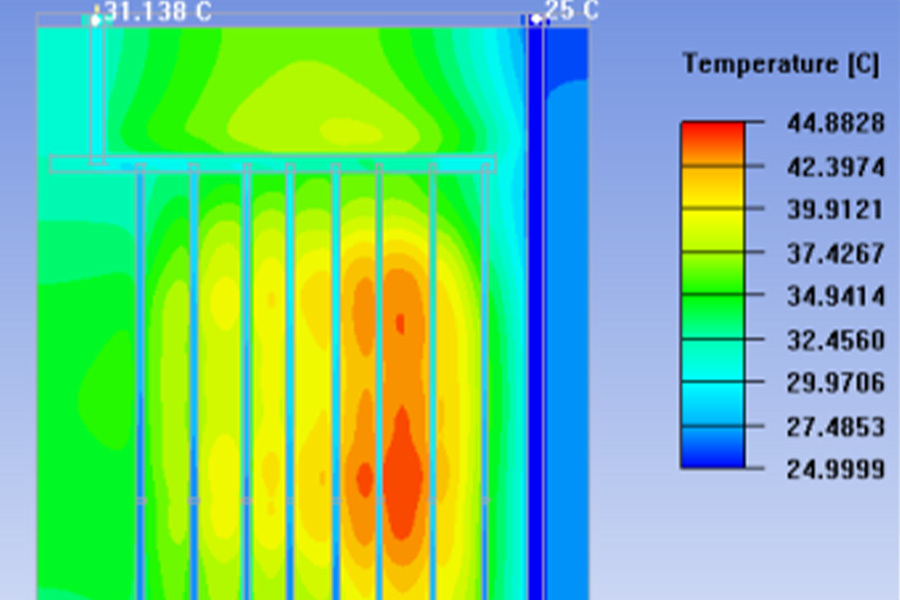
—— Provide thermal simulation analysis according to thermal design goals
—— Optimize heat dissipation solutions based on simulation analysis
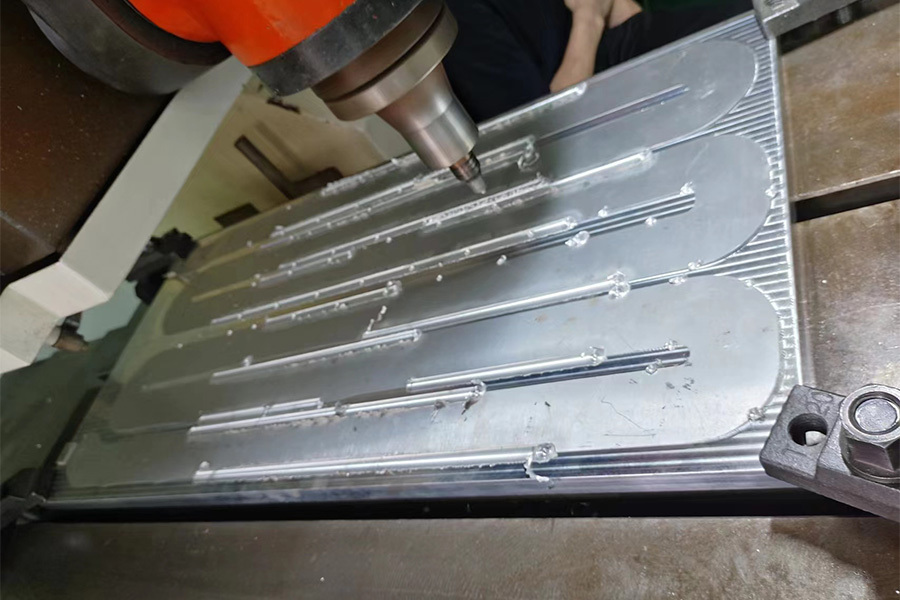
—— Produce air-cooled heat sinks that meet requirements according to drawings
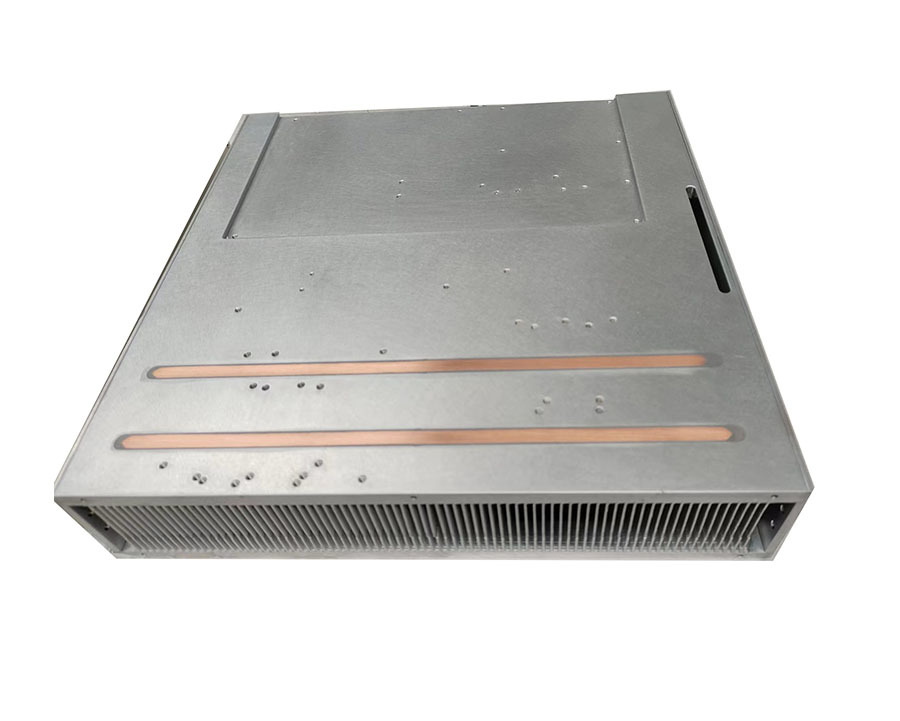
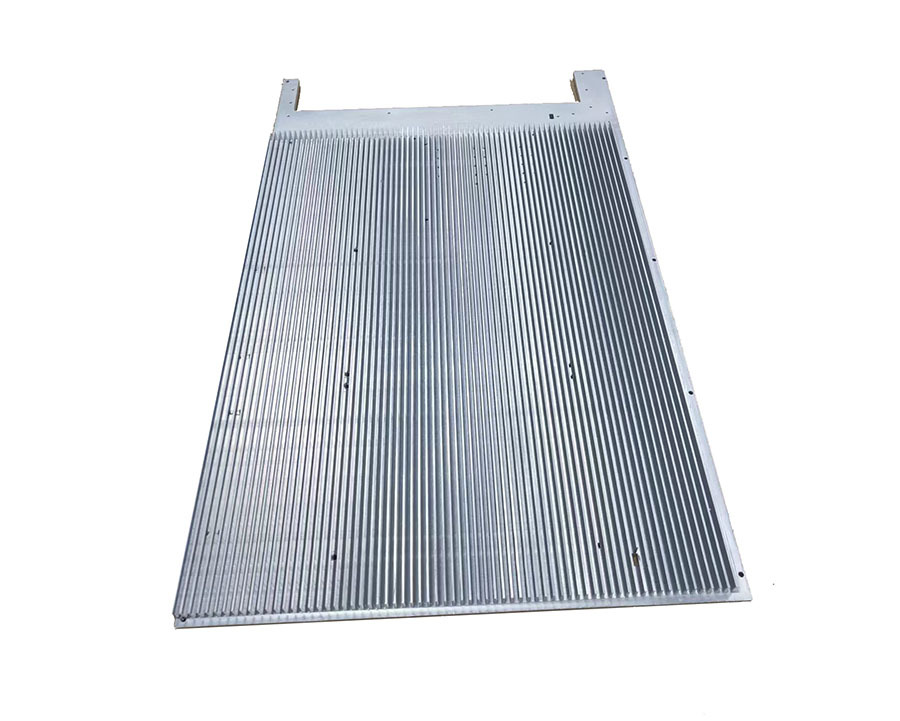
—— And liquid-cooled FSW liquid cooling plates and copper tube liquid cold plates
Laser cooling systems can be divided into the following categories:
1. Water-cooled
The water-cooled laser cooling system is currently the most widely used cooling method. Its principle is to absorb the heat generated by the laser through water, and then take away the heat through water circulation. The water-cooled laser cooling system has the advantages of high cooling efficiency, low noise, and long service life.
2. Air-cooled
The air-cooled laser cooling system blows air directly onto the laser to take away the heat generated by the laser through air. The air-cooled laser cooling system has the advantages of simple structure and easy maintenance, but its cooling efficiency is low and is generally only suitable for low-power lasers.
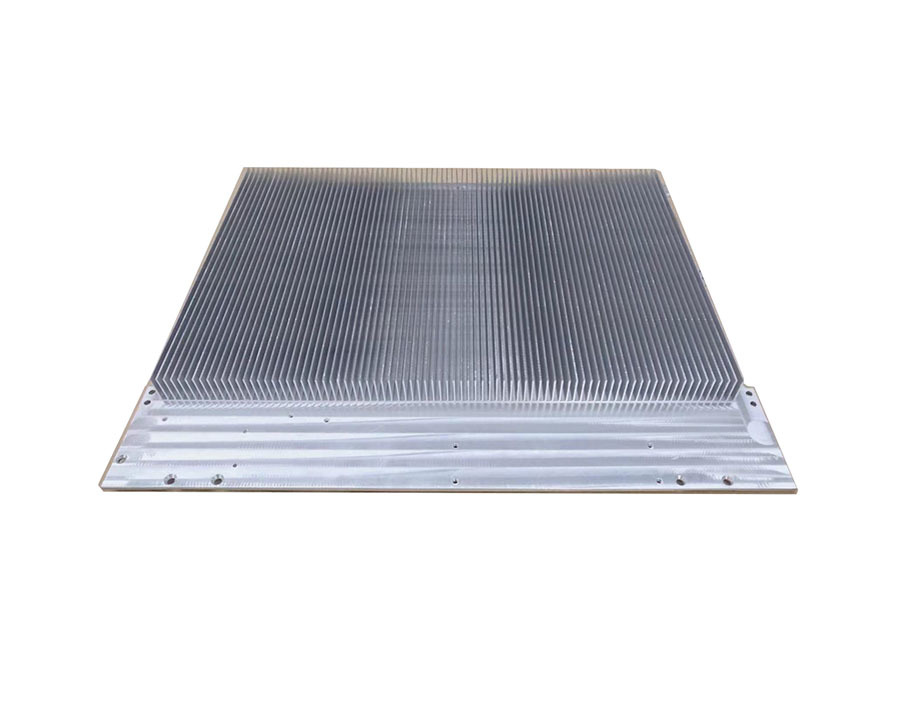
Skived heat sink or embed heat pipes heat sink usually used for the laser air cooling
The heat is mainly dissipated by fans, using metals with good thermal conductivity (such as copper and aluminum) to dissipate the heat through forced convection by fans. This method is suitable for low-power pulsed lasers and continuous lasers.
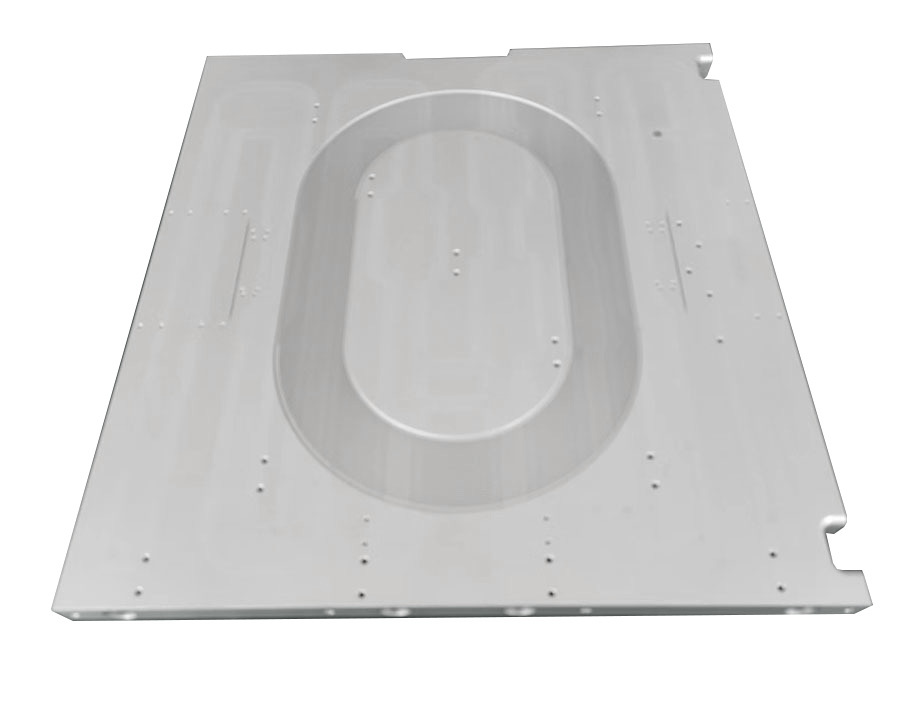
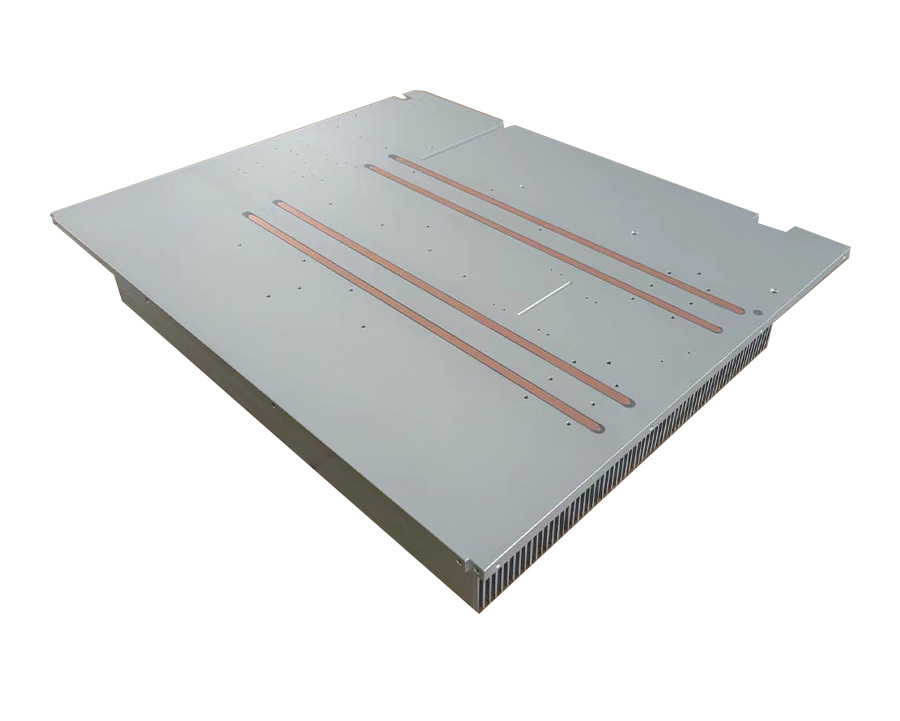
Fiber Laser Water-Cooling Cold Plates
Cooling water circulates in the cooling water path inside the laser to absorb and remove heat. For example, the optical module of the fiber laser is installed with an aluminum alloy base, and the cooling water flows through the holes on the base to dissipate heat for the pump source and optical components.
Under the same temperature and the same area, water transfers dozens of times more heat than air.
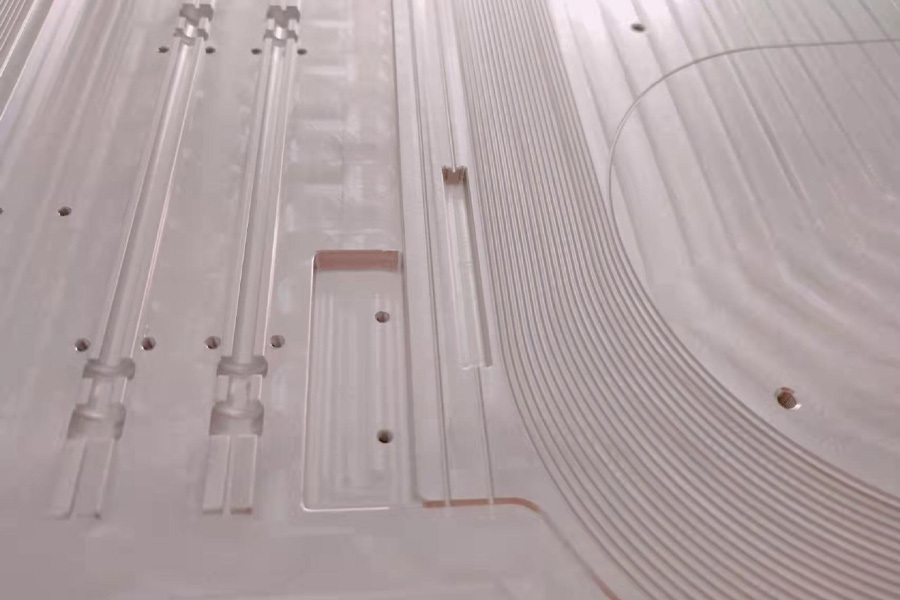
FSW Liquid Cooling Plate Structure
Copper Tube Liquid Cooling Plate Structure
More Varieties Thermal Products: