IGBT Liquid Cold Plates Revolutionize Thermal Management
In the rapidly evolving world of power electronics, thermal management has emerged as a critical bottleneck for performance and reliability. At the heart of this challenge lies the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT), a cornerstone component in applications ranging from electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy systems to industrial motor drives. As power densities soar, traditional air cooling is proving insufficient. Enter the IGBT Liquid Cold Plate—a sophisticated thermal solution that is rapidly becoming the industry standard for managing intense heat loads.
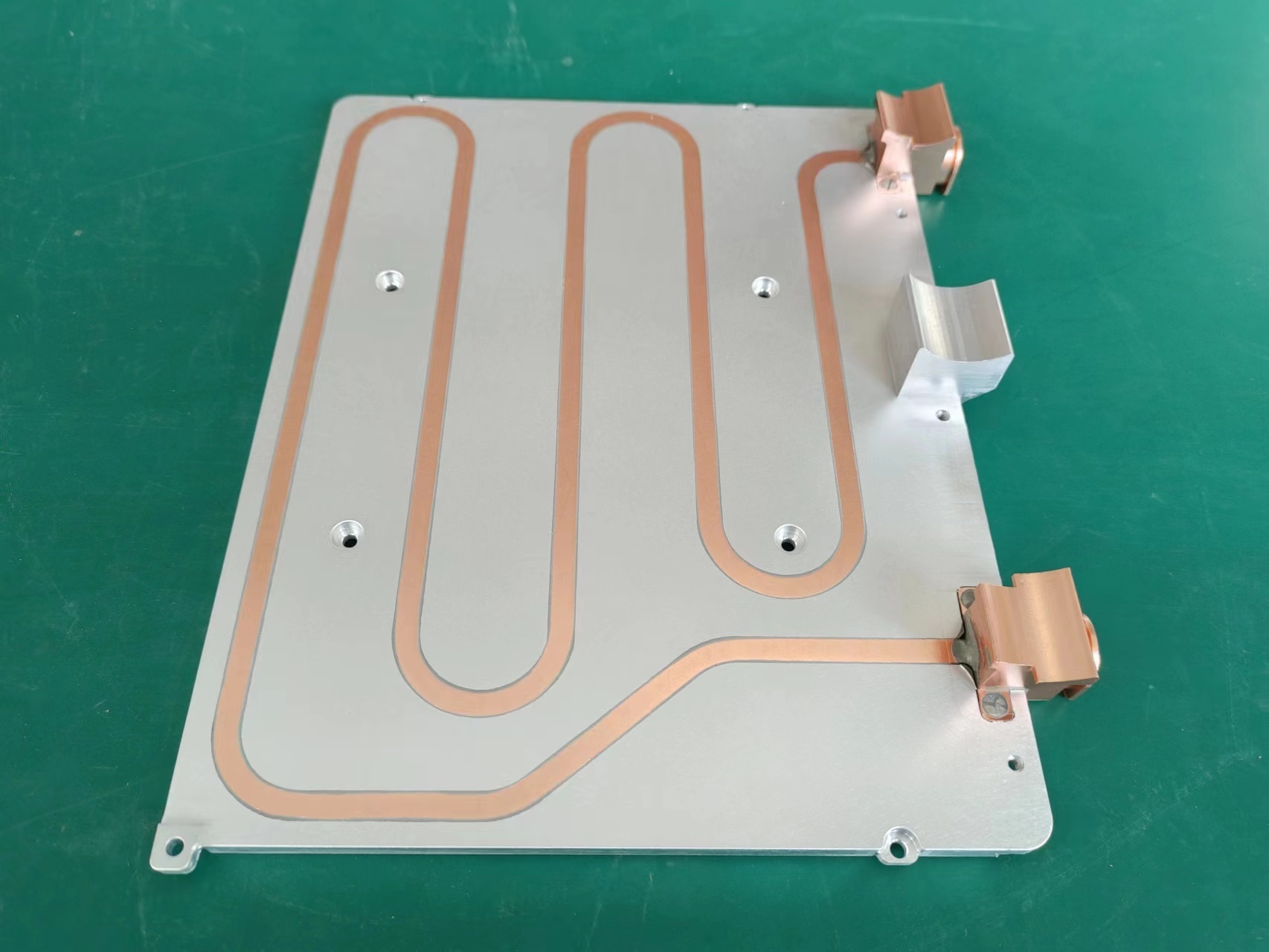
An IGBT Liquid Cold Plate is a dedicated heat exchanger designed to be in direct contact with one or multiple IGBT modules. Its fundamental operation is both efficient and elegant. A coolant fluid, typically a water-glycol mixture, is circulated through internal micro-channels within the plate. This fluid absorbs the immense waste heat generated by the IGBTs during switching operations and transports it away to a secondary radiator, where it is dissipated into the environment. This direct liquid cooling method boasts a thermal conductivity far superior to any air-based system.
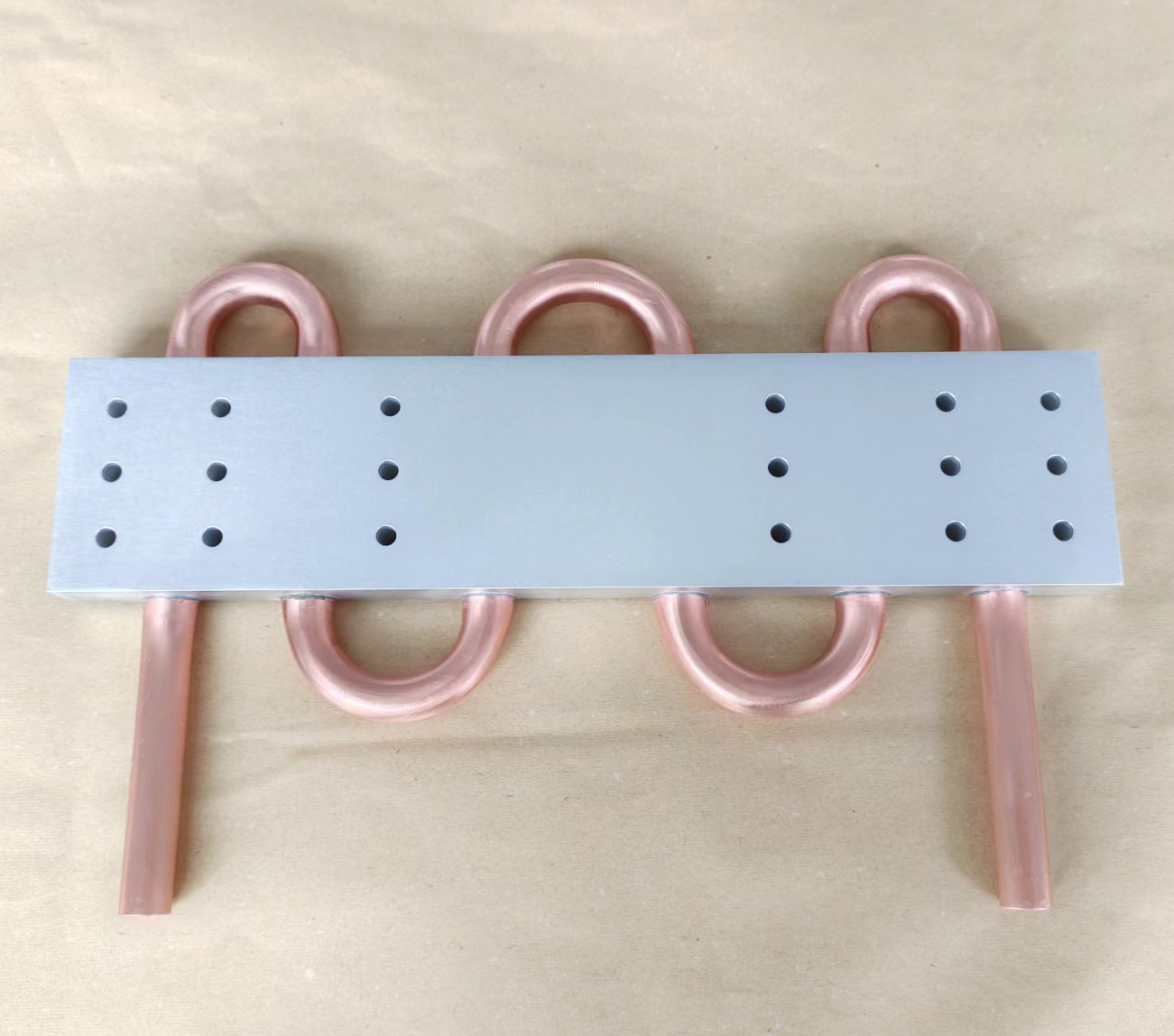

The driving force behind the adoption of this technology is the relentless push for higher power in smaller packages. Modern IGBT modules can generate staggering amounts of heat in a very confined space. An advanced IGBT Liquid Cold Plate can efficiently handle heat fluxes that would cause conventional heat sinks to fail, ensuring the semiconductor operates within its optimal temperature range. This is not merely about preventing failure; it is about maximizing performance. Cooler IGBTs exhibit lower electrical losses, higher efficiency, and significantly longer operational lifetimes. In an electric vehicle inverter, for instance, this translates directly to extended driving range and enhanced reliability.
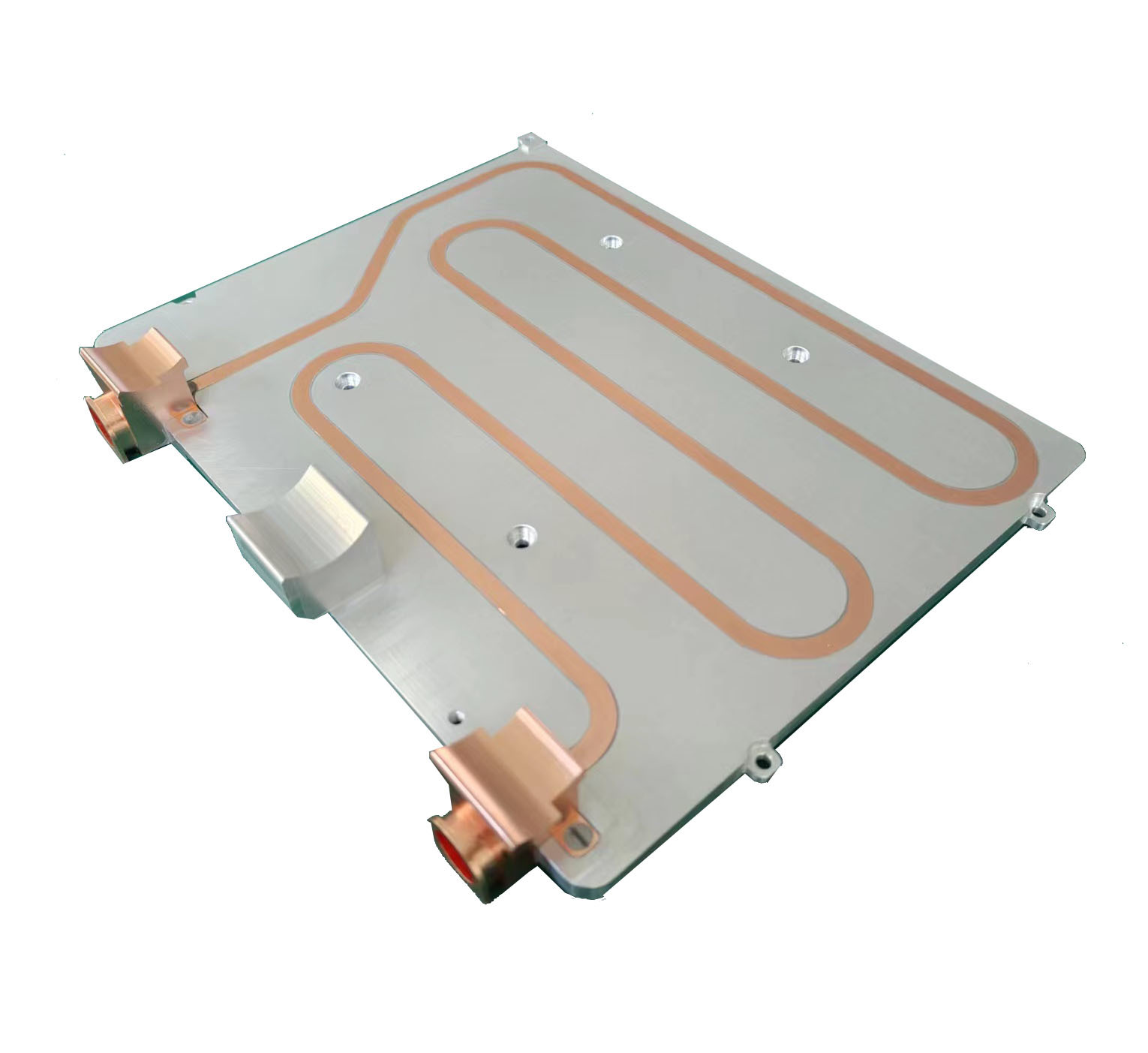

Manufacturing these cold plates requires precision engineering. They are commonly constructed from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper. Techniques like vacuum brazing or friction stir welding are employed to create complex, leak-proof internal channel geometries that maximize the surface area in contact with the coolant. The design is paramount; computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations are used to optimize flow patterns, ensuring even cooling across the entire IGBT Liquid Cold Plate and preventing detrimental hot spots.
The market for these components is experiencing robust growth, fueled by the global transitions toward electrification and green energy. Major players in the automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors are investing heavily in liquid cooling solutions to gain a competitive edge. The development of the IGBT Liquid Cold Plate represents a significant leap forward, enabling the next generation of high-power, high-efficiency electronics that will power our future. As demands continue to intensify, innovation in cold plate technology will remain a hot topic, essential for unlocking the full potential of power semiconductors.
PREVIOUS:
Online Message
Any interest in Vansim.
We'll be appreciate and serve you wholeheartedly , Want to learn more about what we do, have questions or need a quote?






