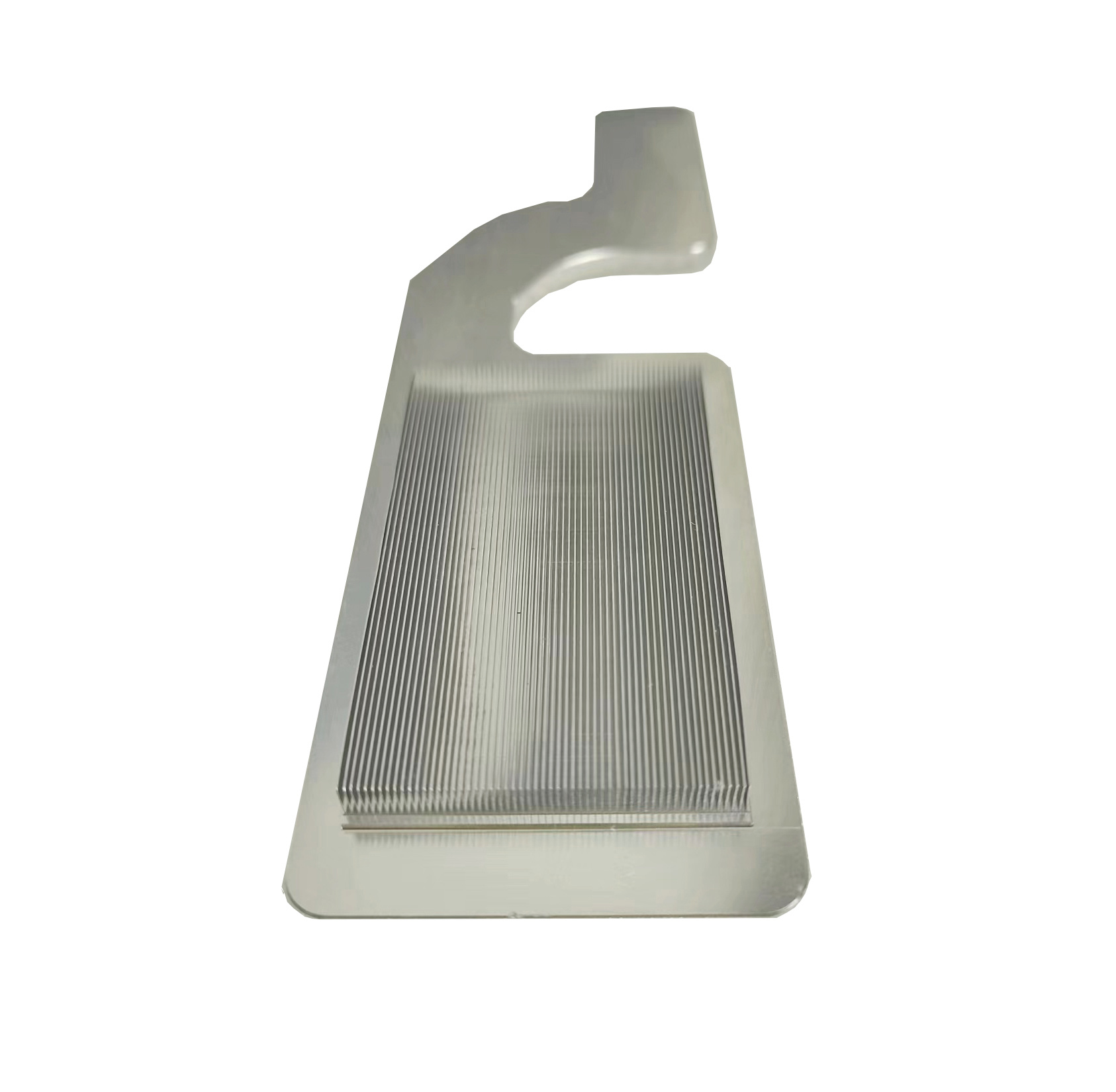
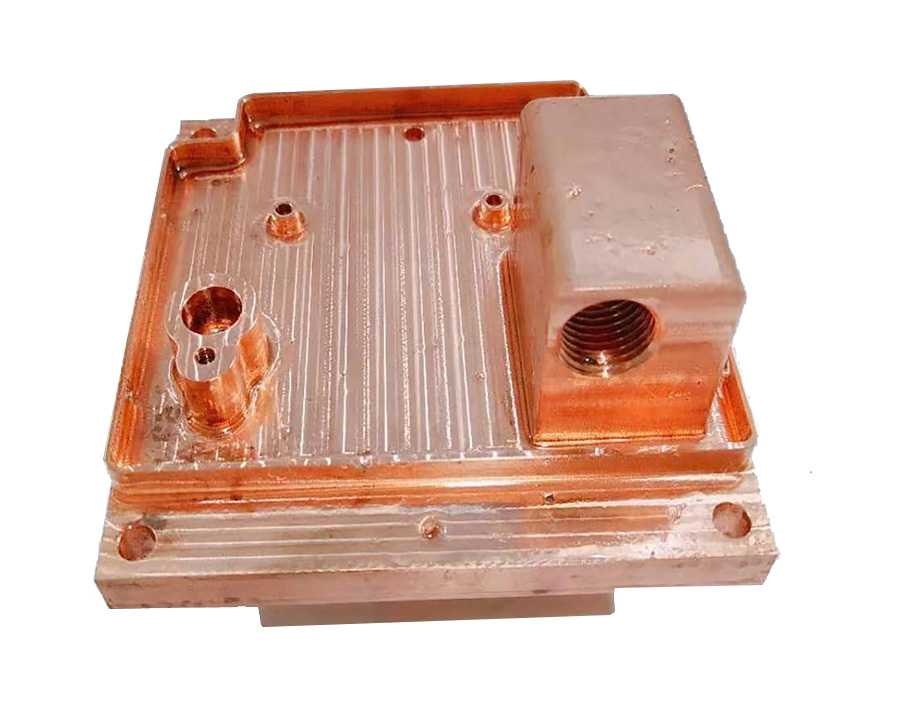
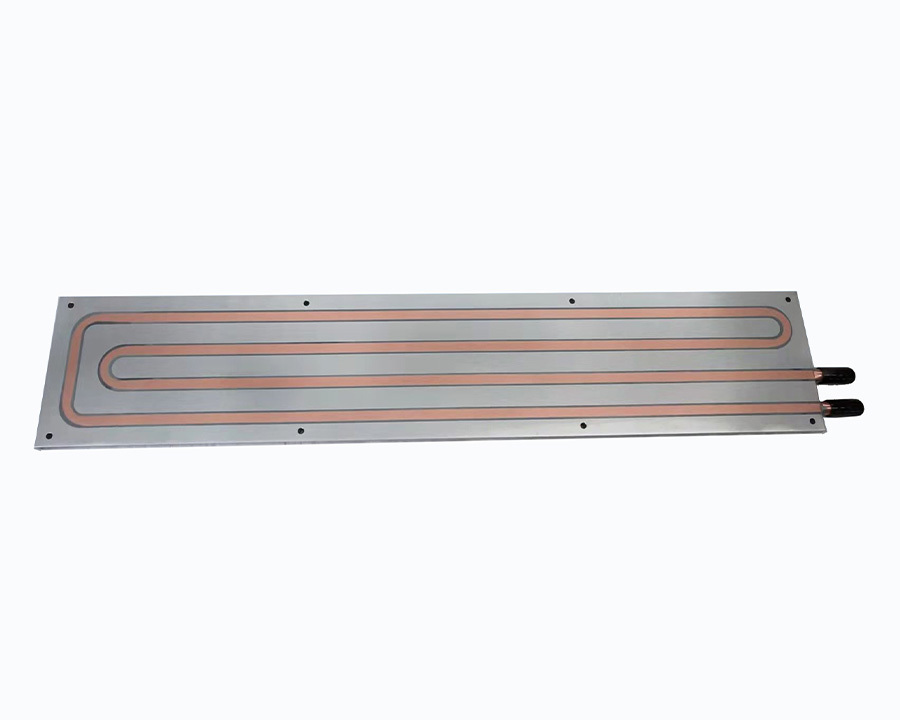
Aluminum Skived Heat Sink for Fiber Laser Air Cooling System with Optical Fiber Slots Machining
1. Product Overview
- High-efficiency heat dissipation via skived fin structure for laser components;
- Integrated optical fiber slots for precise fixing and routing of optical fibers, combining thermal and structural designs.
2. Key Technical Parameters
3. Machining Process Analysis
3.1 Skiving Machining
- Advantages:
- Enables thinner and denser fins (minimum thickness: 0.1 mm) compared to extrusion;
- One-piece fin-base structure eliminates welding thermal resistance for efficient heat transfer.
- Key Steps:
- Secure aluminum baseplate on CNC lathe or specialized skiving equipment;
- Use high-speed rotating tools to machine continuous fins transversely across the baseplate;
- Achieve precision via CNC programming (fin height/pitch tolerance: ±0.05 mm, surface roughness: Ra ≤3.2 μm).
3.2 Optical Fiber Slots Machining
- Process Options:
- Milling: Micro-milling cutters for rectangular/V-shaped slots (positioning accuracy: ±0.02 mm);
- Laser Machining (optional): Femtosecond laser for micron-scale slots with ultra-smooth walls.
- Design Considerations:
- Slot alignment must match fiber routing to avoid excessive bending (minimum curvature radius: ≥20 mm to prevent optical loss);
- Thermal contact gaps at slot bottoms ensure tight fiber-heatsink coupling.
4. Advantages in Fiber Laser Air Cooling Systems
- Enhanced Heat Dissipation:
- Dense fins increase surface area by 30–50% compared to traditional extruded heatsinks;
- Air-cooled design (with axial fans) maintains laser module junction temperature ≤60°C.
- Integrated Structure:
- Slots eliminate separate fiber-clamping components, reducing assembly steps;
- Mechanical protection against fiber abrasion during operation.
- Reliability:
- Lightweight aluminum (density: 2.7 g/cm³) suits airborne or mobile laser systems;
- Anodized surface offers electrical insulation (breakdown voltage ≥500 V) for safety.
5. Typical Applications
- Industrial Laser Machining: Pump modules and gain modules in fiber lasers (20 W–1500 W);
- Scientific & Medical Devices: Compact cooling for lidar systems or laser scalpels;
- Aerospace: High-performance, lightweight cooling for airborne laser systems.



optical fiber cooling skived heat sink
Contact Us
Classification