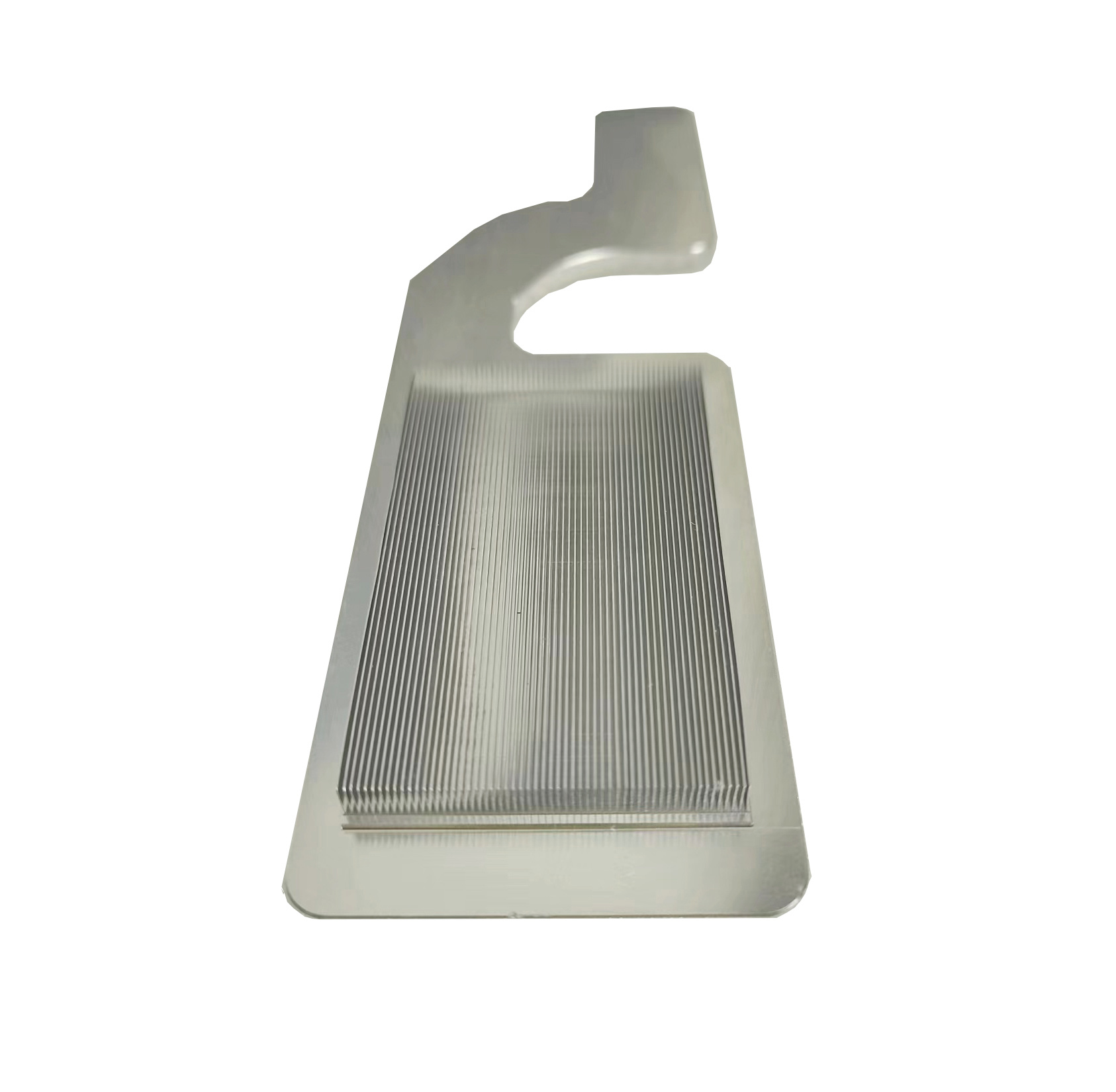
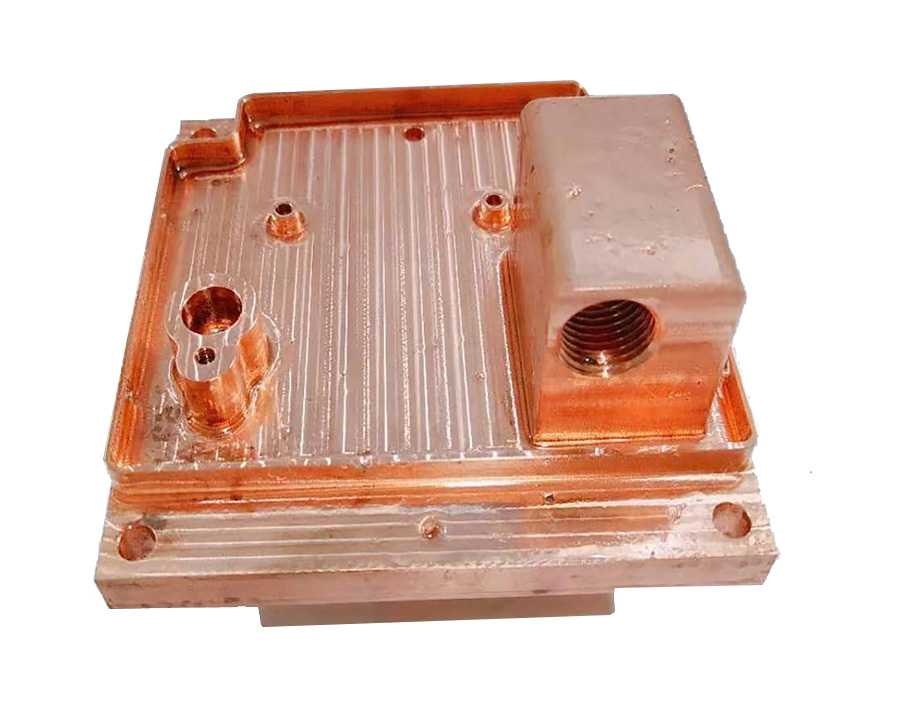
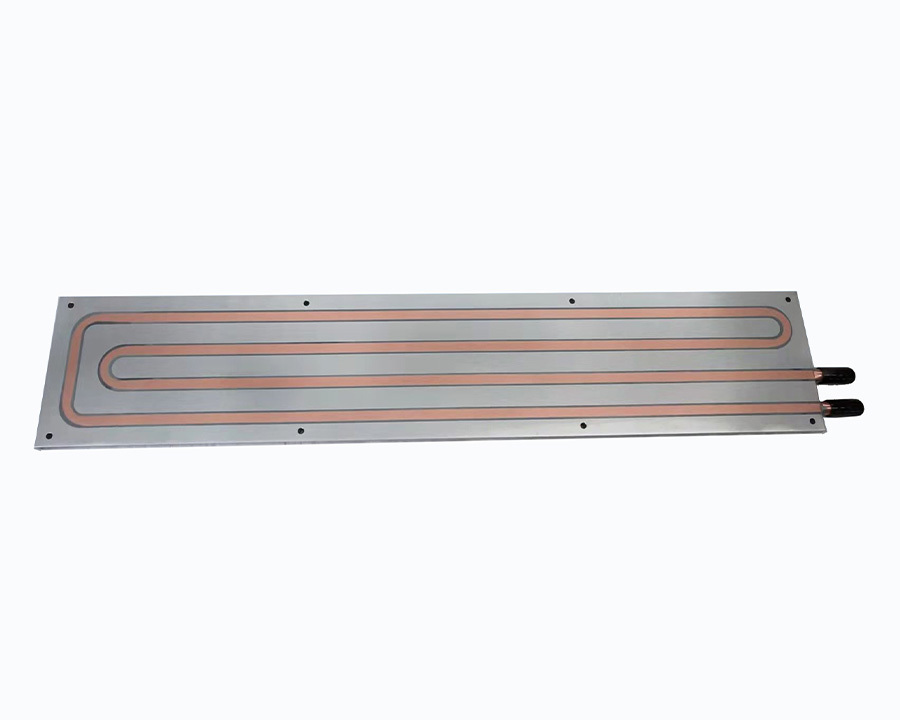
What are the applications of copper skiving fin heat sinks in heat dissipation?
1. Electronics and Consumer Devices
- High-Power Semiconductors:
- Used in power amplifiers, voltage regulators, and microprocessors in servers, gaming PCs, and industrial control systems. The skived fins efficiently dissipate heat from components like CPUs and GPUs to prevent thermal throttling.
- LED Lighting:
- In high-intensity LED fixtures (e.g., streetlights, stadium lights), copper skiving fins cool LED arrays, maintaining light output and longevity by managing junction temperatures.
- Telecommunications Equipment:
- Cooling RF modules, base station amplifiers, and network switches to ensure stable signal transmission in 5G/6G infrastructure.

2. Automotive and Transportation
- Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- Cooling battery packs, inverters, and onboard chargers. Copper’s high thermal conductivity is critical for managing heat in fast-charging systems and high-performance EV motors.
- Engine Electronics:
- Heat sinks for engine control units (ECUs), ignition systems, and hybrid vehicle power management modules.
- Aerospace:
- Lightweight copper skiving fins (often alloyed for strength) cool avionics, radar systems, and satellite components in extreme temperature environments.
3. Industrial and Manufacturing
- Industrial Machinery:
- Cooling variable frequency drives (VFDs), motor control centers (MCCs), and high-power resistors in factory automation systems.
- Renewable Energy:
- In solar inverters and wind turbine converters, where efficient heat dissipation is essential for maximizing energy conversion efficiency.
- Medical Equipment:
- Cooling laser systems, MRI machines, and diagnostic devices (e.g., X-ray generators) to ensure precise operation and safety.

4. Power Generation and Energy
- Power Transformers and Converters:
- Skived fins cool high-voltage transformers and grid-connected inverters in renewable energy plants and data centers.
- Nuclear and High-Temperature Environments:
- Copper alloys (e.g., copper-tungsten) are used in specialized heat sinks for nuclear instrumentation and high-radiation zones, where thermal stability is critical.
5. Cooling Systems and Heat Exchangers
- Liquid-to-Air Heat Exchangers:
- Combined with cold plates or microchannel designs, copper skiving fins enhance heat transfer in loop cooling systems for data centers and high-performance computing (HPC).
- Natural Convection Applications:
- In passive cooling systems (e.g., fanless electronics), the large surface area of skived fins optimizes heat dissipation via air conduction and radiation.
 |  |
6. Advantages of Copper Skiving Fin Heat Sinks
- High Thermal Performance: Copper’s superior conductivity ensures rapid heat transfer from hotspots to fins.
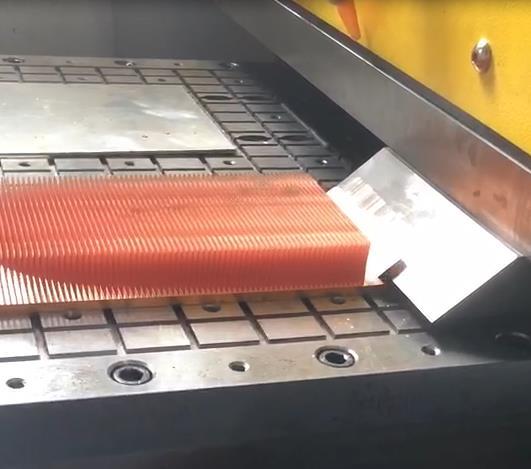
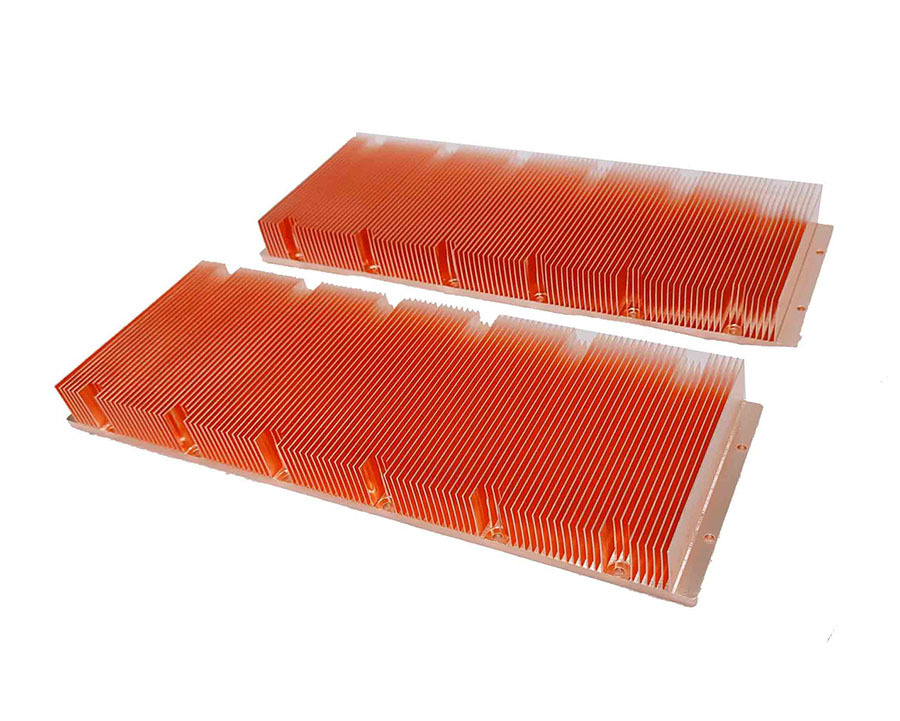
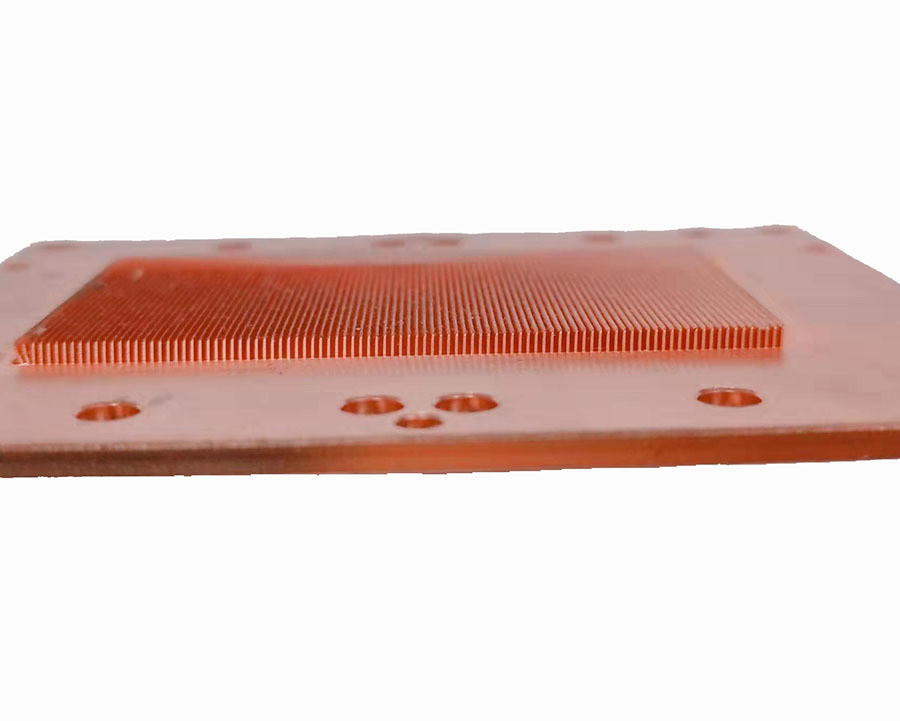
- Customizable Design: Skived fins can be tailored for thickness (0.1–1 mm), height (up to 100 mm), and density, adapting to tight spaces.
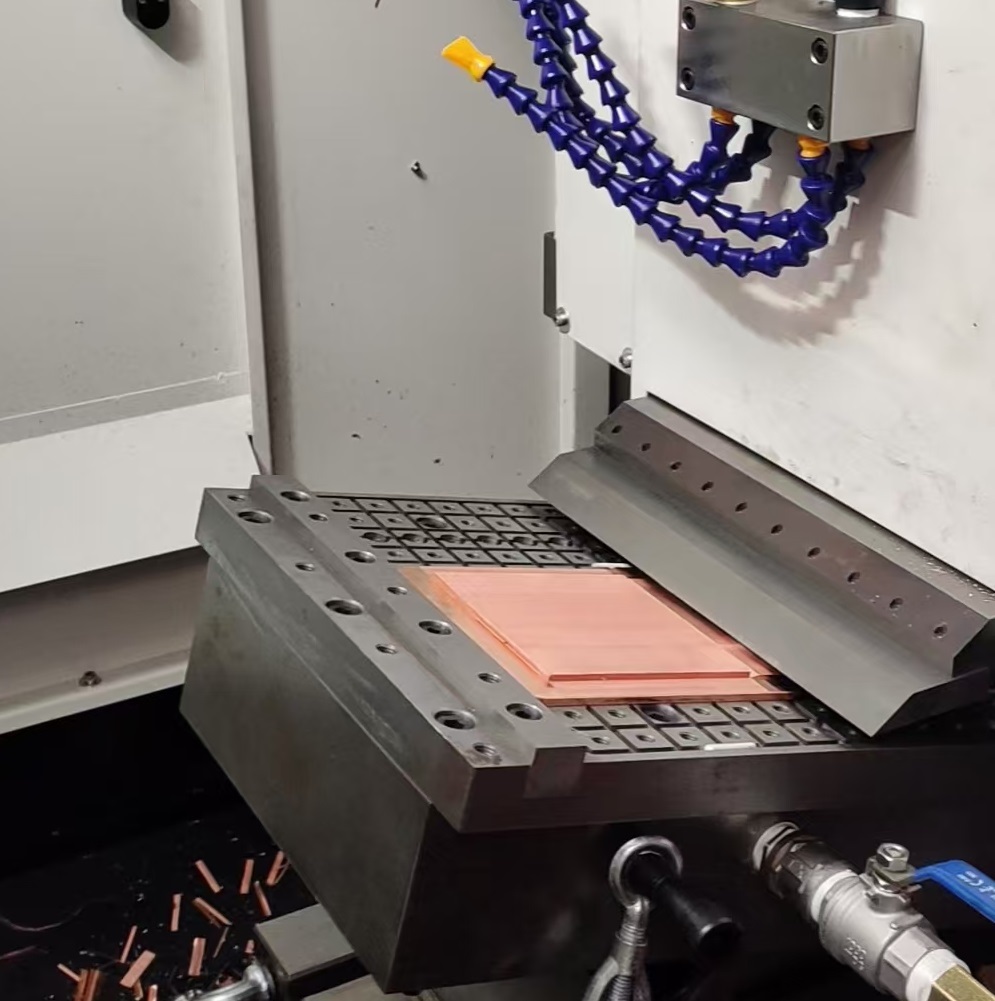
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to extruded or forged fins, skiving (a machining process) offers a balance of performance and affordability for medium-to-high-volume applications.
- Durability: Resistant to corrosion in most environments, suitable for long-term use in harsh conditions.
Limitations and Considerations
- Weight: Copper is denser than aluminum, making it less suitable for ultra-lightweight applications (e.g., drones).
- Oxidation: Surface treatment (e.g., nickel plating) may be required to prevent oxidation in humid environments.
- Cost: More expensive than aluminum, but justified in applications requiring superior thermal performance.
Typical Design Parameters

CPU cooling copper skived heat sink
Contact Us
Classification