What are the application industrial does the FSW cold plates apply for ?
1. FSW cold plate applied for Aerospace and Defense :
- Avionics Cooling: FSW cold plates are critical for cooling radar systems, guidance electronics, and communication modules in aircraft, drones, and satellites. The high-reliability welding of aluminum or copper alloys ensures leak-proof fluid channels in high-vibration environments.
- E-Business Jet Systems: Cooling power electronics in electric propulsion systems, including inverters and battery management units.
- Military Systems: Used in ruggedized cold plates for ground vehicles, naval vessels, and missile systems, where resistance to corrosion (via anodizing or nickel plating) and thermal cycling is non-negotiable.
Technical Drivers: - Weight Constraints: Aluminum FSW cold plates offer high strength-to-weight ratios, essential for aerospace fuel efficiency.
- Environmental Compliance: Chromate-free surface treatments (e.g., zirconium coatings) meet strict aerospace regulations.

2. FSW cold plate applied for Data Centers and High-Performance Computing (HPC)
- Server and GPU Cooling: FSW cold plates are bonded to CPUs, GPUs, and power supplies in rack-mounted servers, dissipating heat from high-density chips (e.g., 300+ W TDP) via liquid cooling loops.
- Immersion Cooling Systems: Submerged cold plates in dielectric fluid baths for supercomputers and AI clusters, where FSW’s leak-proof joints prevent fluid ingress into electronics.
- Edge Computing Nodes: Compact cold plates for distributed computing hubs in remote locations, requiring low maintenance and high reliability.
Technical Drivers: - Thermal Uniformity: FSW’s seamless welds eliminate thermal resistance at joint interfaces, ensuring even heat distribution across large heat sinks.
- Scalability: Modular designs allow easy integration into existing cooling infrastructure (e.g., cold/hot aisle containment systems).
3. FSW cold plate applied for Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Automotive
- Battery Thermal Management (BTMS): FSW cold plates are embedded in EV battery packs to cool lithium-ion cells, preventing thermal runaway and maintaining optimal operating temperatures (25–40°C).
- Inverter and Motor Cooling: Cooling silicon carbide (SiC) inverters and permanent magnet motors in hybrid/electric vehicles, where high power density demands efficient heat removal.
- Fuel Cell Systems: Used in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles to manage heat from proton exchange membrane (PEM) stacks, ensuring consistent energy output.
Technical Drivers: - Vibration Resistance: FSW’s solid-state welding minimizes fatigue failures in dynamic vehicle environments.
- Material Compatibility: Aluminum cold plates with nickel plating enable corrosion resistance in salt-exposed road conditions.
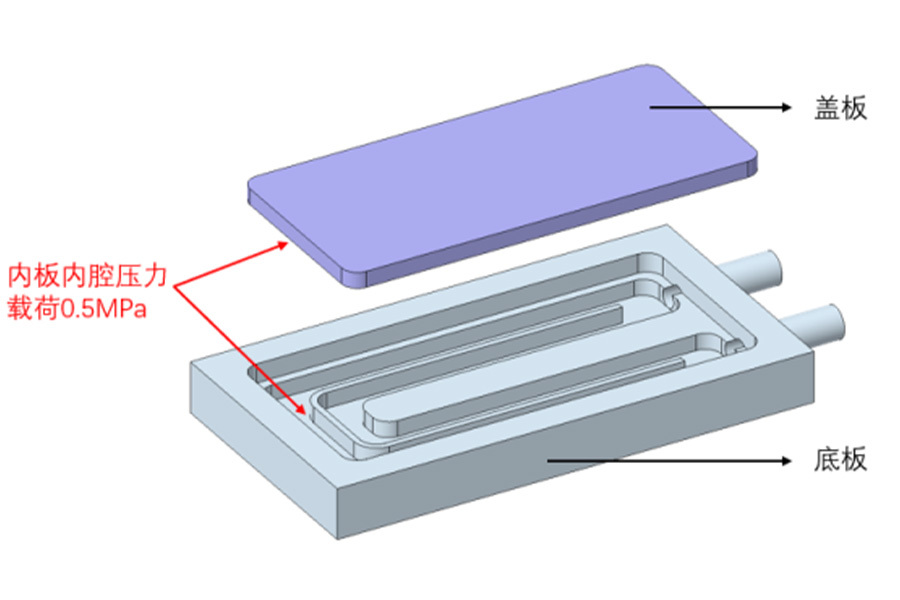
4. FSW cold plate applied for Industrial Machinery and Renewable Energy
- Industrial Automation: Cooling servo motors, PLCs, and variable frequency drives (VFDs) in factory robotics and CNC machines, ensuring uninterrupted operation in high-duty cycles.
- Solar Inverters: FSW cold plates dissipate heat from IGBTs in solar power inverters, improving energy conversion efficiency in utility-scale solar farms.
- Wind Turbines: Cooling power electronics and gearbox lubrication systems in offshore wind turbines, where saltwater corrosion resistance (via hard anodizing) is critical.
Technical Drivers: - Durability: FSW cold plates withstand prolonged exposure to dust, moisture, and temperature fluctuations in industrial settings.
- Custom Geometry: Complex fluid channel designs (e.g., serpentine or pin-fin structures) optimize heat transfer for unique machinery layouts.
5. FSW cold plate applied for Consumer Electronics and Telecommunications
- 5G Base Stations: Cooling power amplifiers and phased-array antennas in outdoor 5G nodes, where compact FSW cold plates integrate with forced-air or loop-cooling systems.
- Gaming Consoles and Laptops: High-end devices use micro-channel FSW cold plates for vapor chamber or heat pipe integration, addressing thermal throttling in portable electronics.
- LED Lighting: Industrial-grade LED fixtures (e.g., stadium lights) employ FSW cold plates to manage heat and extend lamp lifespan.
Technical Drivers: - Form Factor: Thin-profile cold plates (≤3 mm) fit into space-constrained enclosures, a key advantage over brazed alternatives.
- Aesthetics: Dyed anodized finishes (e.g., black or silver) meet consumer design requirements while enhancing heat dissipation.

6. FSW cold plate applied for Medical Equipment and Biotechnology
- MRI and CT Scanners: Cooling superconducting magnets and electronics in diagnostic imaging systems, requiring non-magnetic materials (e.g., aluminum) and hermetic seals.
- Laboratory Instruments: Cold plates in centrifuges, PCR machines, and bioreactors maintain precise temperature control for biological samples.
- Wearable Medical Devices: Miniaturized FSW cold plates in portable dialysis units or insulin pumps ensure reliable thermal management in compact designs.
Technical Drivers: - Biocompatibility: Electropolished surfaces and non-toxic coatings (e.g., passivated stainless steel for specialty cold plates) meet ISO 10993 standards.
- Leak Prevention: FSW’s zero-porosity welds are critical in sterile environments to avoid fluid contamination.




liquid cooling FSW process cold plate
Contact Us
Classification