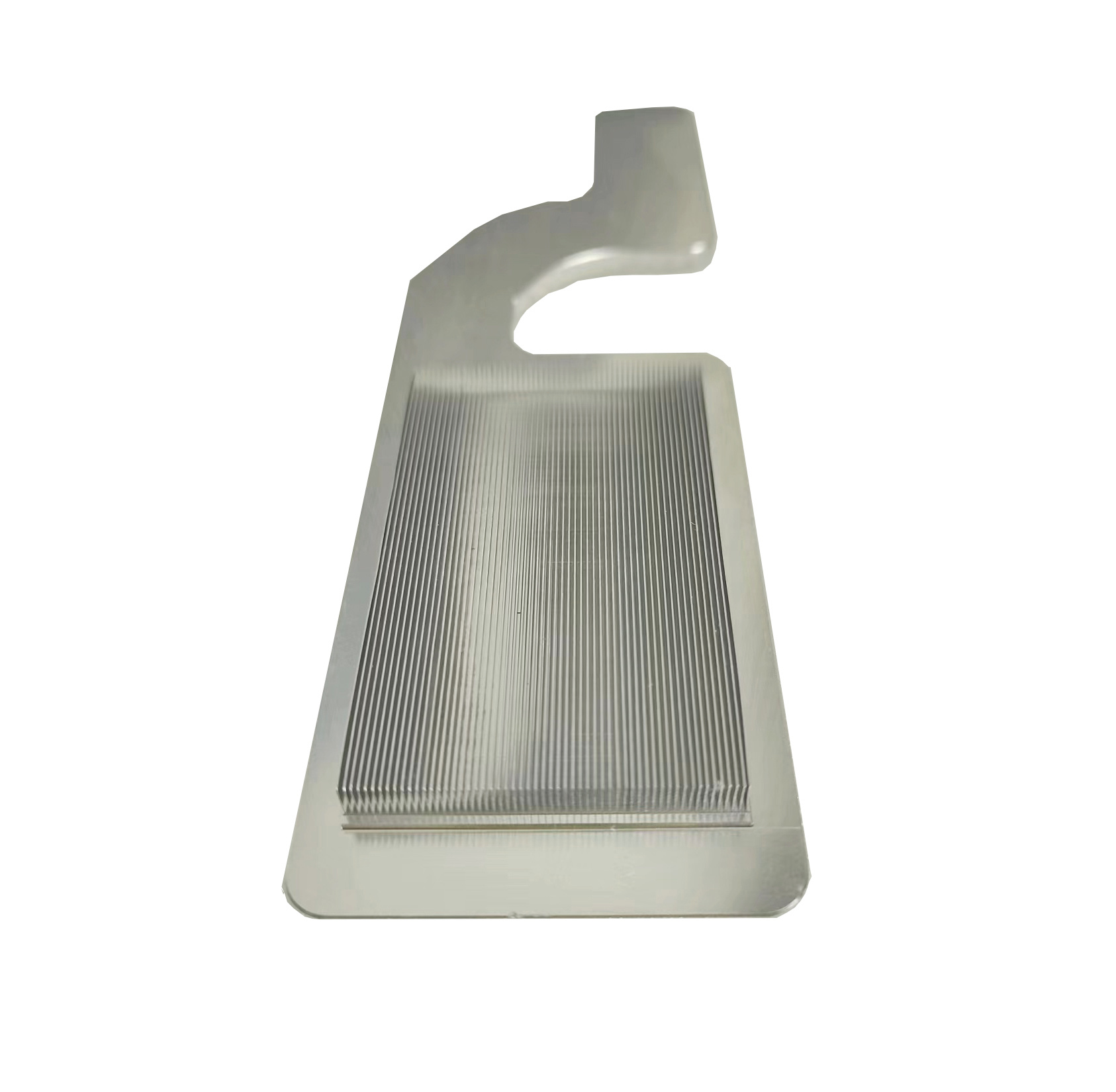
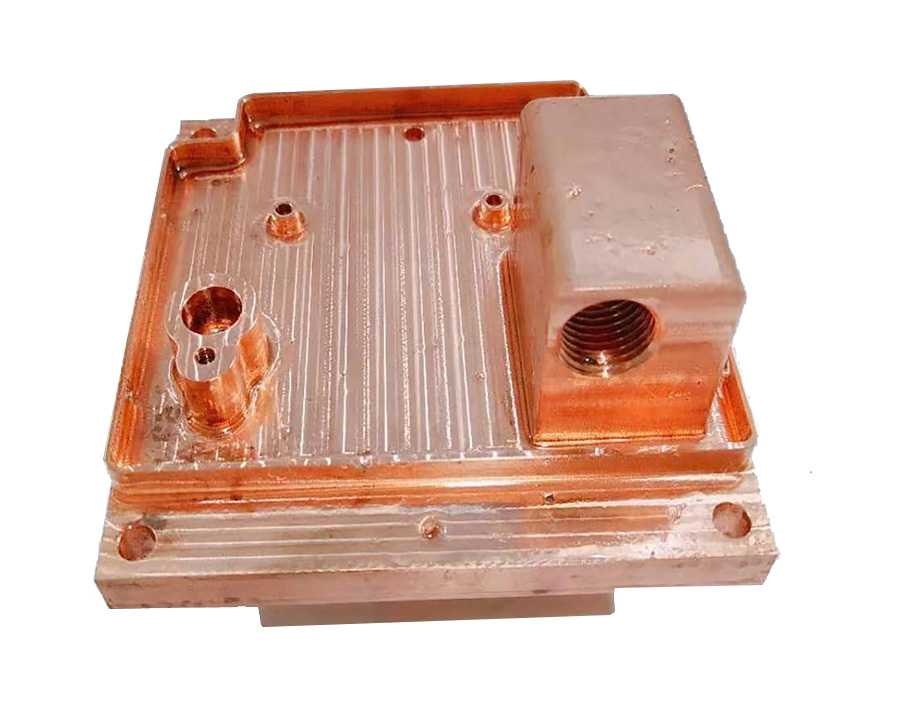
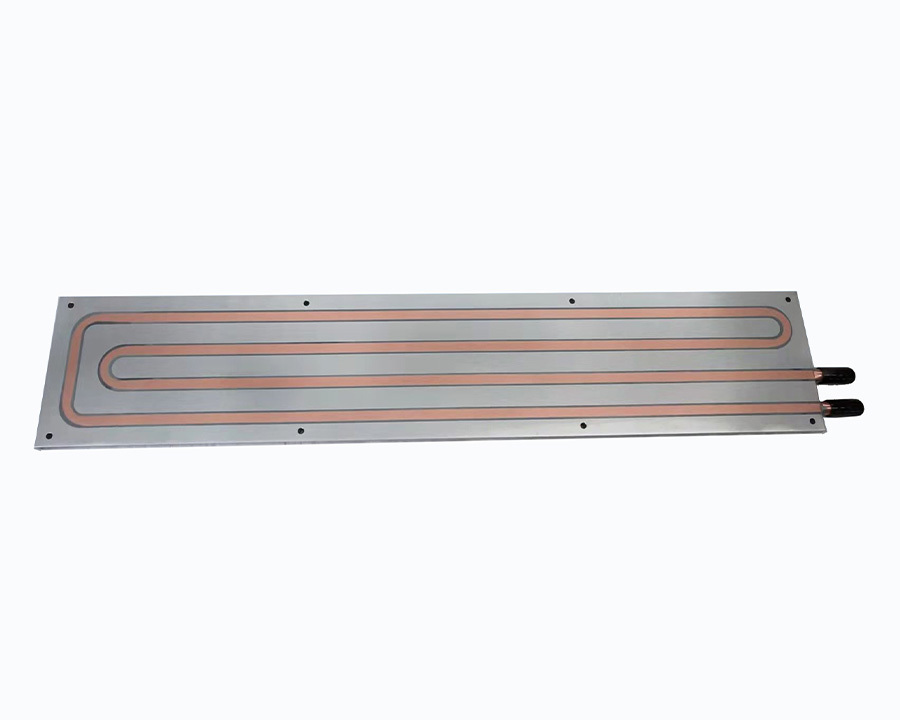
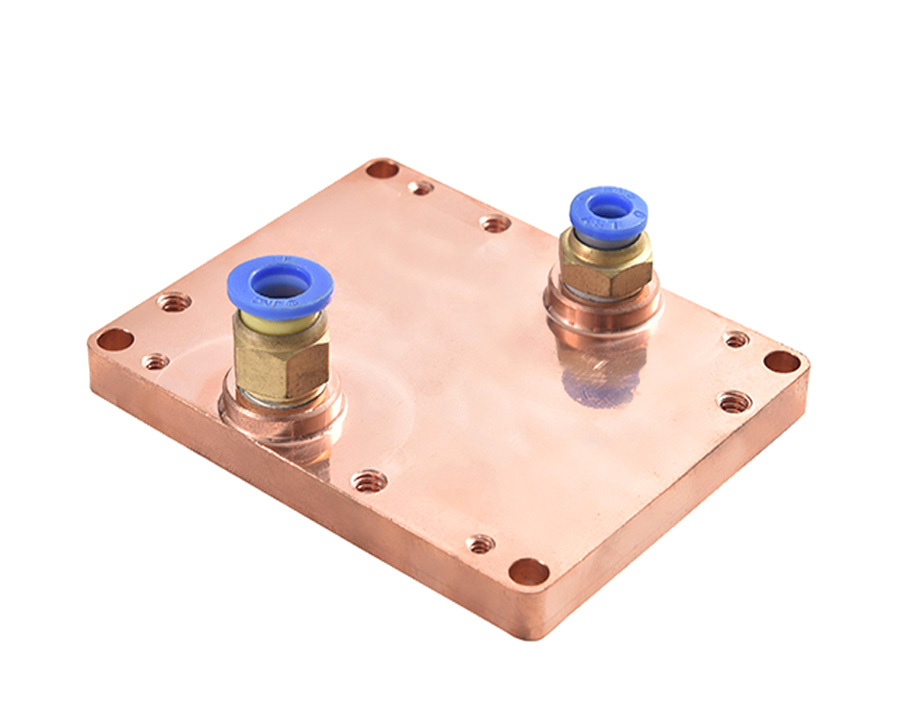
1. What material usually used for the FSW process for the cold plate?
2. The channel base machining and cover machining

3. The key process is Friction Stir Welding (FSW) for the FSW cold plates
- Fixturing: The two machined halves (with channel faces facing each other) are clamped tightly in a custom fixture to prevent movement during welding.
- Tool Setup: A rotating FSW tool with a profiled shoulder and pin (made of high-strength materials like H13 tool steel or tungsten carbide) is used. The tool’s speed (RPM) and traverse rate are optimized for material thickness and alloy.
- Welding Process: The tool is plunged into the joint line, and the rotating shoulder generates frictional heat, plasticizing the aluminum. The pin stirs the plasticized material, forming a dense, defect-free weld as the tool moves along the joint.
4. Post-Weld Machining and Finishing
- Flatness Correction: The welded assembly may be milled or ground to flatten surfaces, especially if minor warping occurred during FSW.
- Port Machining: Inlet/outlet ports for fluid connections are drilled and tapped (e.g., NPT or metric threads) using CNC machining, ensuring tight tolerances for leak-proof fittings.
- Surface Treatment: To enhance corrosion resistance and thermal interface compatibility, the exterior may be:
- Anodized (e.g., Type II or Type III anodizing for a durable oxide layer).
5. The Quality Control of FSW cold plate is the Pressure Testing
- LeakageTesting: The cold plate is sealed, filled with water (or air at low pressure), and pressure test used to be 6-bar to 1.5Mpa) for 5–10 minutes. Sensors or visual inspection detect leaks.
- Non-Destructive Evaluation (NDE):
- Dye Penetrant Inspection to check for surface cracks in welds.
- Ultrasonic Testing to assess internal weld quality, such as voids or incomplete penetration.
- Flow Testing: Optional flow validation ensures fluid passes through channels without abnormal resistance, using flow meters or pressure drop measurements.
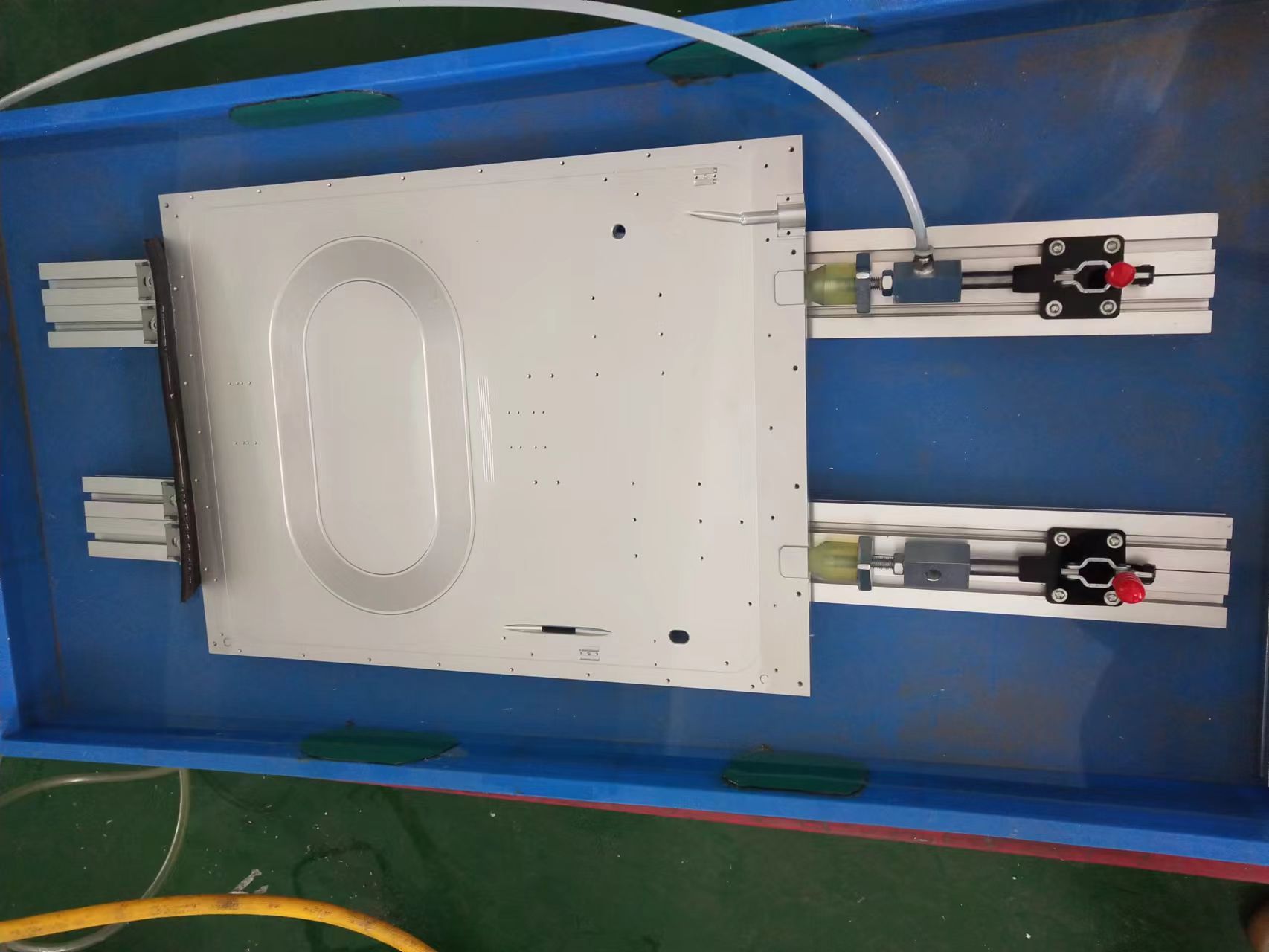



Liquid cooling system FSW liquid cold plate
Contact Us
Classification