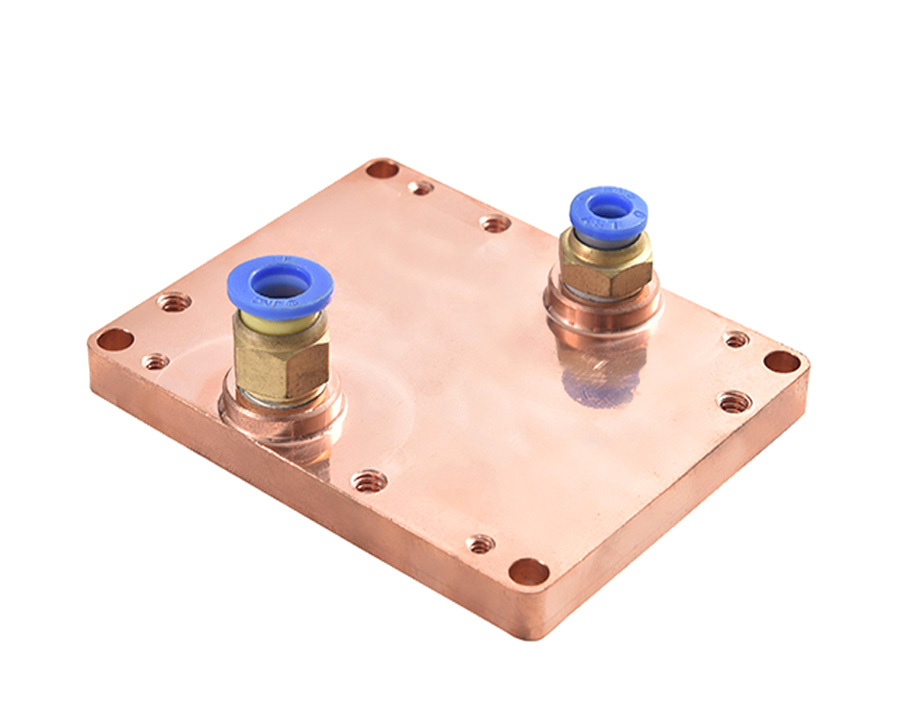
Vansim (Dongguan)Hardware Products Co., Ltd.


What's the manufacturing characteristic of copper skived heat sinks for CPU air cooling?
1. Material Selection
- Base Material:
- High-purity copper (e.g., C11000 electrolytic tough pitch copper, thermal conductivity ≈401 W/m·K) is used for superior heat transfer.
- Copper alloys (e.g., C10100 oxygen-free copper) may be preferred for ultra-high conductivity in extreme applications.
- Material Form:
- Typically starts as a solid copper block or slab (thickness: 10–30 mm) with uniform grain structure to ensure consistent machining performance.
2. Skiving fin Process Basics
(1) Machine Setup
- Single-Point Cutting Tool:
- A high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide blade with a sharp edge (radius ≤0.02 mm) and precise angle (e.g., rake angle: 5–15°, clearance angle: 2–5°) is used.
- The blade is mounted on a spindle that rotates at high speed (e.g., 1000–3000 RPM) while the copper block is fed linearly (feed rate: 0.1–0.5 mm/rev).
- Coolant/Lubricant:
- Water-based or synthetic coolants are applied to reduce friction, dissipate heat, and improve surface finish (avoids blade wear and copper smearin
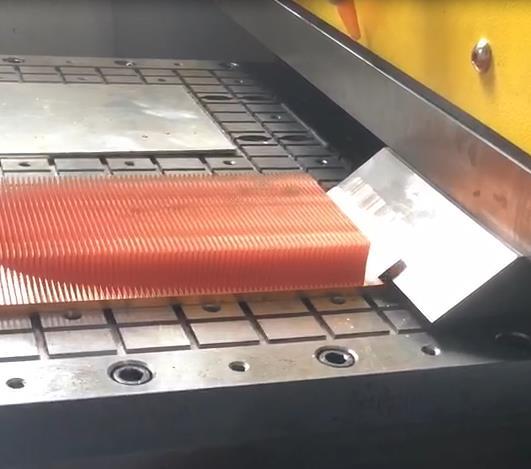

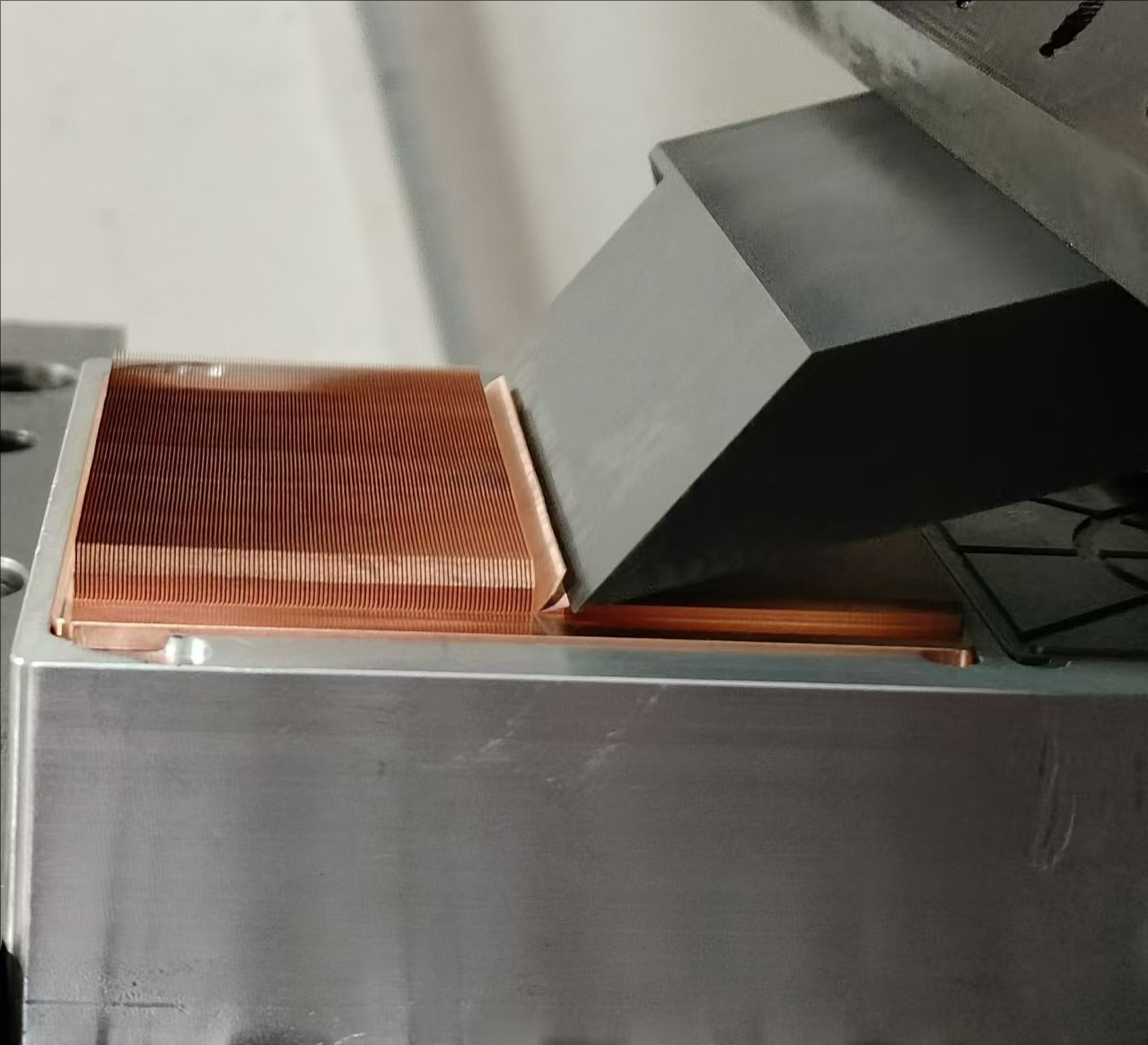
- Water-based or synthetic coolants are applied to reduce friction, dissipate heat, and improve surface finish (avoids blade wear and copper smearin
(2) Fin Geometry Control
- Fin Thickness:
- Typically 0.05–0.8 mm (thinner fins increase surface area but risk bending or breaking).
- Achieved by adjusting the blade depth of cut (DOC) and feed rate.
- Fin Height:
- Ranges from 2–50 mm (limited by the copper block’s initial thickness and structural stability).
- Taller fins require stiffer tooling to prevent vibration-induced defects.
- Fin Pitch (Spacing):
- Usually 1.0–3.0 mm (dependent on airflow requirements; tighter pitches improve heat dissipation but reduce airflow).
- Controlled by the linear feed rate of the copper block.
(3) Surface Finish and Tolerance
- Roughness (Ra):
- A smooth finish (Ra ≤1.6 μm) is critical to minimize air resistance and enhance heat transfer (rough surfaces trap boundary layer air).
- Dimensional Tolerance:
- Fin thickness and pitch must be precise (±0.05 mm) to ensure uniform airflow and compatibility with CPU heat spreaders.
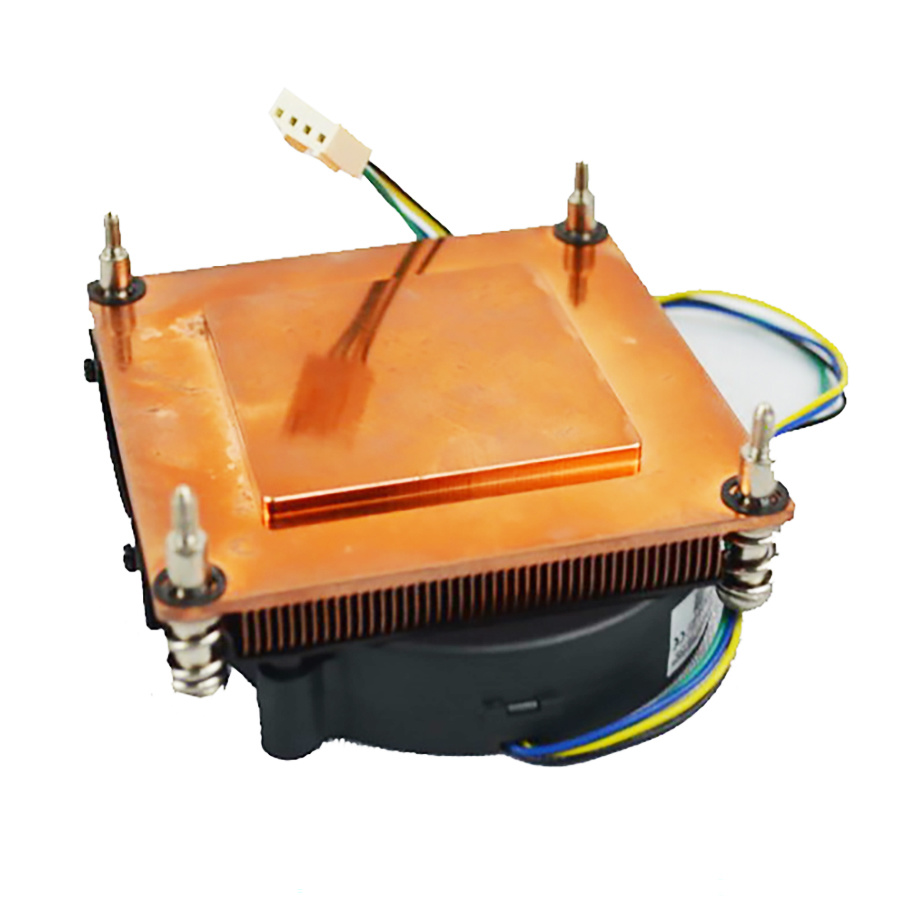
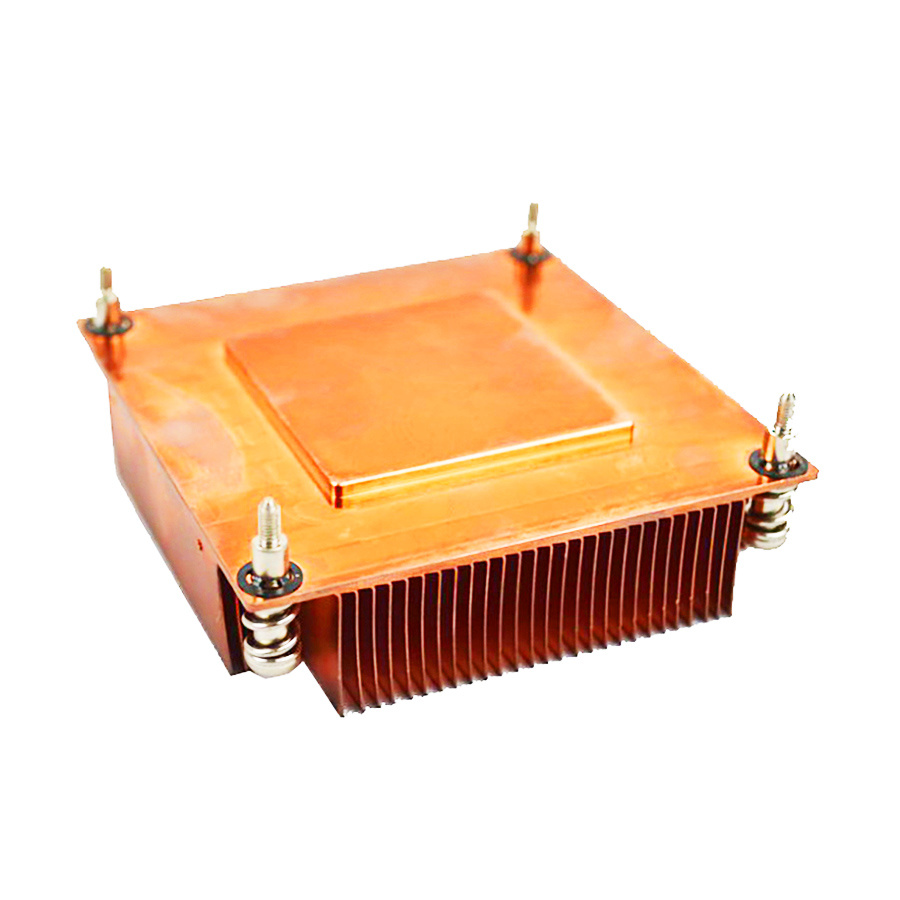

3. Design and Structural Considerations
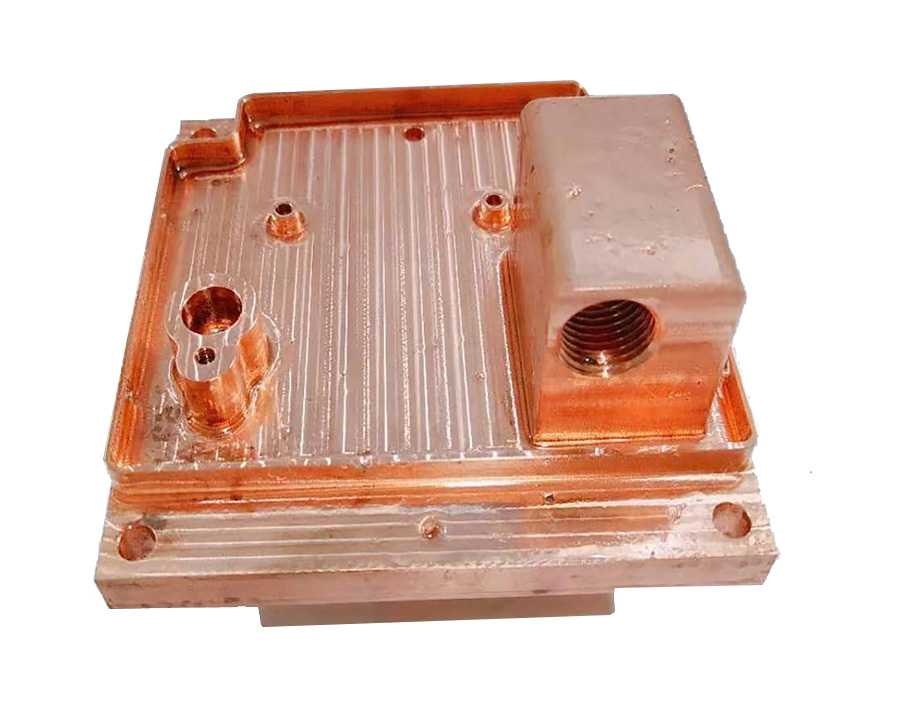
(1) Base Plate Integration
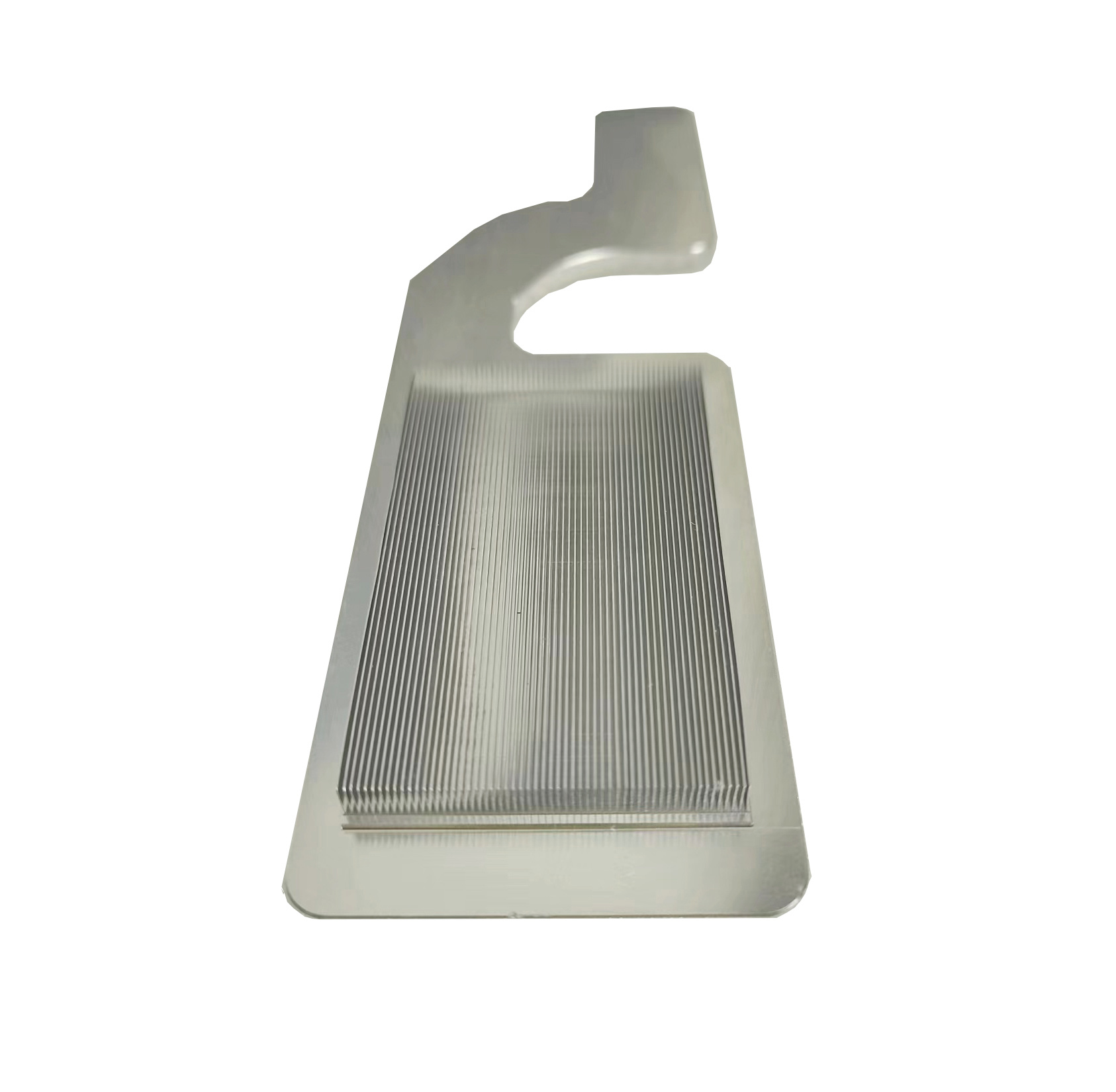
- The skived fins are integral to the base plate, creating a monolithic structure with minimal thermal interface resistance (unlike bonded or soldered fins).
- The base plate thickness (3–5 mm) is optimized for direct contact with the CPU (via thermal paste) and to evenly distribute heat to the fins.
(2) Airflow Optimization
- Asymmetric Fin Shapes:
- Fins may be tapered or angled (e.g., 5–15°) to guide airflow and reduce turbulence.
- Chamfered Edges:
- Rounded or chamfered fin tips (0.1–0.3 mm radius) minimize air resistance and noise.
- Fin Alignment:
- Fins are aligned parallel to the airflow direction (e.g., perpendicular to the CPU fan) for optimal convective heat transfer.
(3) Thermal Performance Limits
- Heat Flux Constraints:
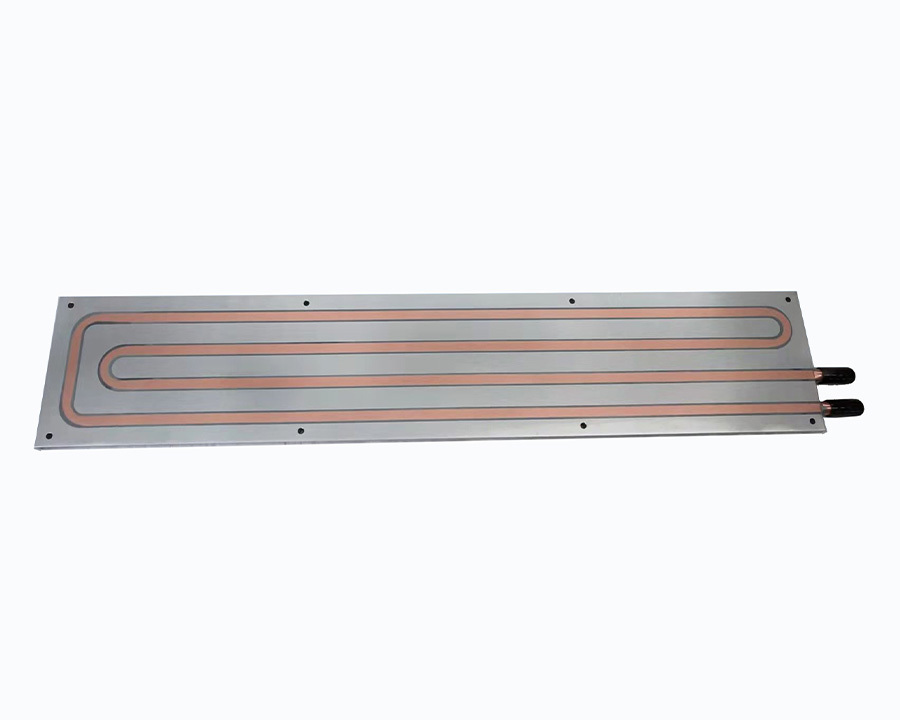
- Copper’s high conductivity allows efficient heat spreading, but skived fins may struggle with ultra-high power CPUs (>250 W) without additional features like embedded heat pipes or vapor chambers.
4. Post-Processing Steps
(1) Deburring and Straightening
- Mechanical Deburring:
- Fins are brushed or tumbled to remove burrs from cutting edges (critical for safety and airflow).
- Thermal Stress Relief:
- Annealing (heating to 200–300°C for 1–2 hours) may be used to relieve machining-induced stresses and prevent fin warping.
(2) Surface Treatment
- Nickel Plating:
- Applied to prevent oxidation (copper tarnishes easily) and improve compatibility with solder (if integrating heat pipes later).
- Black Anodization (for Aluminum-Copper Hybrids):
- In rare cases, copper fins may be bonded to an aluminum base, with anodization enhancing corrosion resistance (though pure copper sinks typically skip anodizing).
(3) Quality Control
- Visual Inspection:
- Check for bent fins, uneven spacing, or blade marks that could disrupt airflow.
- Thermal Testing:
- Use a heat source (e.g., simulated CPU) and an airflow rig to measure temperature rise and pressure drop across the sink.
5. Advantages of Skived Copper Fins
- Monolithic Structure:
- No thermal interface resistance between fins and base, unlike bonded or stamped fins.
- High Aspect Ratio Fins:
- Thin, tall fins maximize surface area without compromising structural integrity (vs. extruded or folded fins).
- Design Flexibility:
- Custom fin geometries (e.g., varying pitch or thickness along the sink) can be tailored for specific CPU layouts.
- Scalability:
- Suitable for mass production with automated CNC skiving machines (lower cost than extruded copper fins for low-to-medium volumes).
6. Challenges and Limitations
- Material Waste:
- Skiving generates significant copper swarf (up to 30% material loss), increasing costs (mitigated by recycling).
- Tool Wear:
- Carbide blades degrade after machining ~50–100 sinks, requiring frequent replacement (HSS blades last fewer cycles).
- Fin Thickness Limits( Vansim's skiving fin capability can manufacturing the fins thickness as min as 0.05mm):
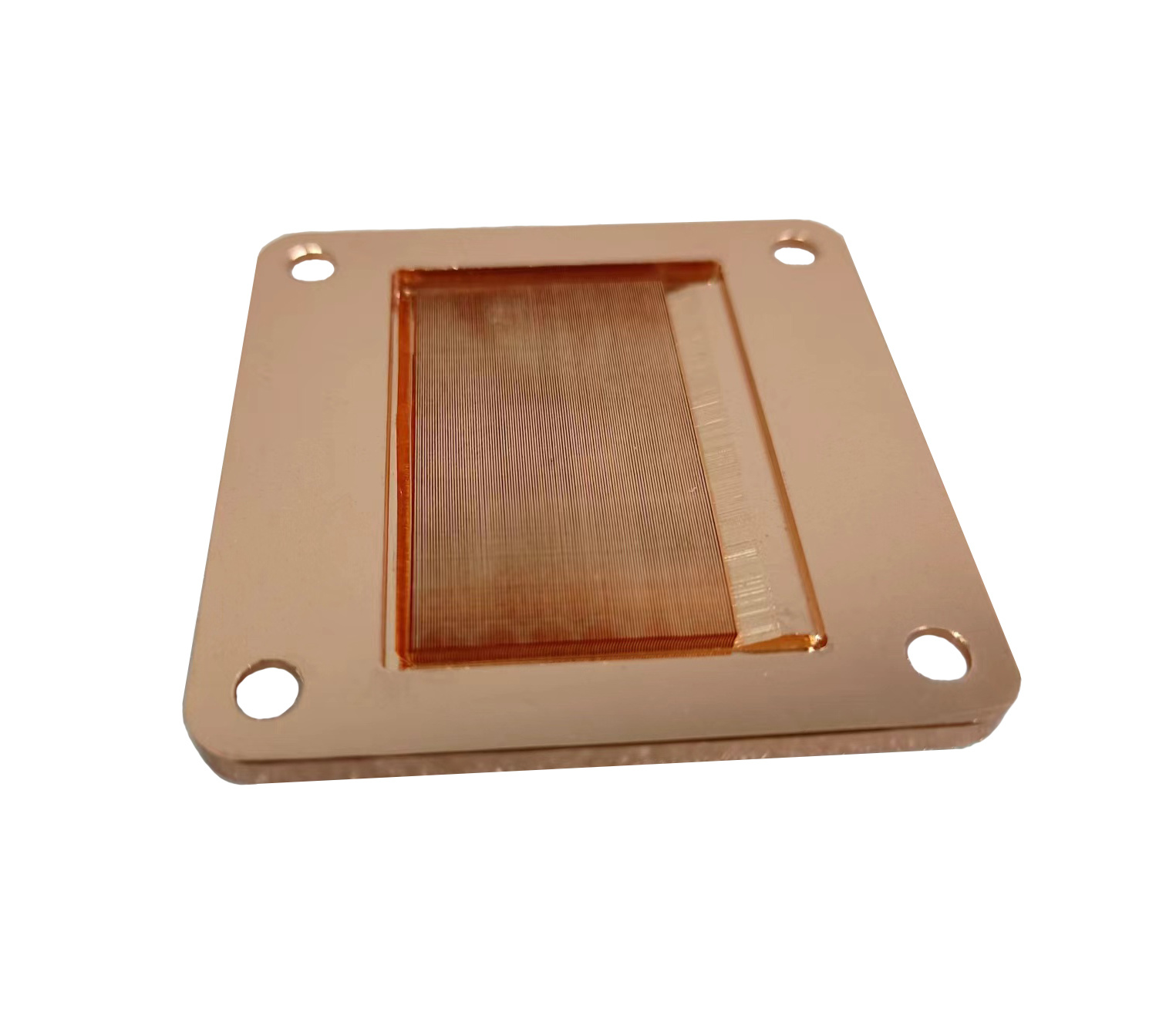

- Below ~0.2 mm, fins are prone to tearing or excessive burring, limiting surface area gains.
- Thermal Bottlenecks:
- For CPUs >200 W, skived copper alone may not suffice; hybrid designs (copper skived fins + heat pipes) are often used.
7. Comparison with Alternative Technologies
| Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Skived Copper | High thermal conductivity, monolithic design | High material cost, moderate heat flux limit |
| Extruded Aluminum | Low cost, high production speed | Lower thermal conductivity |
| Stamped Fins | Complex geometries, low waste | Thermal interface resistance |
| Additive Manufacturing | Custom shapes, minimal waste | High cost, limited thermal performance |


CPU cooling copper skived heat sink
Contact Us
// CONTACT US
Didn'T Find The Service You Want?
For inquiries about our products, please email to us and we will be in touch within 24 hours.
We Support Customization
Continue To Create Greater Value For Customers
Contact Us

No. 10, Minying West Road, Hengli Town, Dongguan City, China 523390
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
These cookies are necessary for basic functions such as payment. Standard cookies cannot be turned off and do not store any of your information.
These cookies collect information, such as how many people are using our site or which pages are popular, to help us improve the customer experience. Turning these cookies off will mean we can't collect information to improve your experience.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies help us understand what you are interested in so that we can show you relevant advertising on other websites. Turning these cookies off will mean we are unable to show you any personalized advertising.